搜索到
12
篇与
的结果
-
 Spring AI 实战:调用本地 Tool 工具方法实现大模型能力扩展 前言大模型虽强,但在实时信息获取(如当前日期、天气)、复杂计算等场景下存在局限。而 Tool 工具方法 正是解决这一问题的关键 —— 它让大模型能调用本地代码获取结果,弥补自身能力短板。本文将通过具体代码案例,手把手教你在 Spring AI 中集成本地 Tool,实现大模型与本地逻辑的联动。一、基础准备:Spring AI 调用大模型环境搭建在集成 Tool 前,先搭建 Spring AI 调用大模型的基础环境,确保能正常与大模型交互。1. 添加核心依赖在 pom.xml 中引入 Spring AI OpenAI 适配器依赖(兼容主流大模型平台):<!-- Spring AI 大模型接入核心依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId> <artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-openai</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>2. 基础调用代码实现(1)Controller:定义接口入口创建一个简单的 HTTP 接口,接收用户提问并调用服务层处理:import com.yeeiee.ailogic.module.ai.service.chat.SpringAiTestService; import jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @RestController @RequestMapping("ai-test") public class SpringAiTestController { @Resource private SpringAiTestService springAiTestService; // 流式输出接口(支持实时返回大模型响应) @GetMapping(value = "stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE) public Flux<String> stream(@RequestParam("content") String content) { return springAiTestService.stream(content); } }(2)Service:实现大模型调用逻辑定义服务接口及实现类,配置大模型连接信息并发起调用:// 服务接口 public interface SpringAiTestService { // 大模型流式输出方法 Flux<String> stream(String content); } // 服务实现类 import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil; import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatResponse; import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt; import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiChatModel; import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiChatOptions; import org.springframework.ai.openai.api.OpenAiApi; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @Service public class SpringAiTestServiceImpl implements SpringAiTestService { @Override public Flux<String> stream(String content) { // 配置大模型平台(以硅基流动为例,兼容 OpenAI 接口格式) OpenAiChatModel chatModel = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .openAiApi(OpenAiApi.builder() .baseUrl("https://api.siliconflow.cn") // 硅基流动 API 地址 .apiKey(System.getenv("SiliconFlow_API")) // 从环境变量获取 API Key .build()) .defaultOptions(OpenAiChatOptions.builder() .model("Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507") // 指定模型 .build()) .build(); // 构建提问并发起流式调用 Prompt prompt = new Prompt(content); Flux<ChatResponse> stream = chatModel.stream(prompt); // 处理响应流,提取文本内容 return stream.map(chunk -> { String text = chunk.getResult() != null && chunk.getResult().getOutput() != null ? chunk.getResult().getOutput().getText() : ""; return StrUtil.nullToDefault(text, ""); // 避免 null 结果 }); } }3. 未集成 Tool 时的问题当我们调用接口提问 “今天是几号?” 时,大模型因无实时能力,回答明显不准确:这正是需要 Tool 工具方法的场景 —— 让大模型调用本地代码获取真实日期。二、核心实现:集成本地 Tool 工具方法通过 Spring AI 的 Tool 机制,让大模型在需要时自动调用本地代码(如获取当前日期),步骤如下:1. 创建本地 Tool 工具类定义一个获取当前日期的工具类,交给 Spring 管理(需实现 Function 接口):import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonClassDescription; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.function.Function; /** * 本地 Tool:获取当前日期 */ @Slf4j @Component("current_date") // 组件名称,用于后续指定 Tool public class CurrentDateToolFunction implements Function<CurrentDateToolFunction.Request, CurrentDateToolFunction.Response> { // 工具方法请求参数(无参数时为空类) @Data @JsonClassDescription("查询今天的日期") // 描述工具用途,帮助大模型理解 public static class Request { } // 工具方法响应结果 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public static class Response { private String date; // 日期结果(格式:yyyy-MM-dd) } // 核心逻辑:获取当前日期并返回 @Override public Response apply(Request request) { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); String currentDate = dateFormat.format(new Date()); log.info("调用本地 Tool 获取当前日期:{}", currentDate); return new Response(currentDate); } }关键说明:类上添加 @Component("current_date"),指定 Tool 名称为 current_date;Request 和 Response 类用于定义工具的输入输出格式,需配合 JSON 注解描述用途;apply 方法实现具体逻辑(此处为获取当前日期)。2. 修改大模型配置,启用 Tool在 Service 实现类中,为大模型配置 Tool 相关参数,使其能调用本地工具:@Override public Flux<String> stream(String content) { // 配置大模型,添加 Tool 支持 OpenAiChatModel chatModel = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .openAiApi(OpenAiApi.builder() .baseUrl("https://api.siliconflow.cn") .apiKey(System.getenv("SiliconFlow_API")) .build()) .defaultOptions(OpenAiChatOptions.builder() .model("Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507") .toolNames("current_date") // 指定启用的 Tool 名称(对应@Component的value) .build()) .toolCallingManager(SpringUtil.getBean(ToolCallingManager.class)) // 注入 Tool 调用管理器(Spring AI 提供) .build(); // 后续调用逻辑与之前一致... Prompt prompt = new Prompt(content); Flux<ChatResponse> stream = chatModel.stream(prompt); return stream.map(chunk -> { String text = chunk.getResult() != null && chunk.getResult().getOutput() != null ? chunk.getResult().getOutput().getText() : ""; return StrUtil.nullToDefault(text, ""); }); }核心配置:toolNames("current_date"):告诉大模型可调用名为 current_date 的 Tool;toolCallingManager:注入 Spring AI 提供的 ToolCallingManager,负责处理 Tool 调用流程。三、测试验证:Tool 工具调用效果再次调用接口提问 “今天是几号?”,大模型会自动触发 current_date 工具调用:1. 大模型响应结果大模型先说明 “将调用工具获取日期”,随后返回通过本地代码获取的准确日期。2. 本地日志验证查看应用日志,确认 Tool 被成功调用:2025-08-20 15:19:44.637 | INFO 28998 | boundedElastic-1 [TID: N/A] c.y.a.m.a.s.m.t.CurrentDateToolFunction | 调用本地 Tool 获取当前日期:2025-08-20总结通过本文案例,我们实现了 Spring AI 与本地 Tool 工具的集成,核心步骤可概括为:定义 Tool 工具类(实现 Function 接口,交给 Spring 管理);在大模型配置中指定 Tool 名称和调用管理器;大模型会根据提问自动判断是否调用 Tool,获取结果后整理回答。这种方式让大模型突破了自身局限,能灵活扩展实时数据获取、复杂计算等能力。下一篇将深入源码解析 Spring AI Tool 的底层实现原理,敬请期待!
Spring AI 实战:调用本地 Tool 工具方法实现大模型能力扩展 前言大模型虽强,但在实时信息获取(如当前日期、天气)、复杂计算等场景下存在局限。而 Tool 工具方法 正是解决这一问题的关键 —— 它让大模型能调用本地代码获取结果,弥补自身能力短板。本文将通过具体代码案例,手把手教你在 Spring AI 中集成本地 Tool,实现大模型与本地逻辑的联动。一、基础准备:Spring AI 调用大模型环境搭建在集成 Tool 前,先搭建 Spring AI 调用大模型的基础环境,确保能正常与大模型交互。1. 添加核心依赖在 pom.xml 中引入 Spring AI OpenAI 适配器依赖(兼容主流大模型平台):<!-- Spring AI 大模型接入核心依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId> <artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-openai</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>2. 基础调用代码实现(1)Controller:定义接口入口创建一个简单的 HTTP 接口,接收用户提问并调用服务层处理:import com.yeeiee.ailogic.module.ai.service.chat.SpringAiTestService; import jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @RestController @RequestMapping("ai-test") public class SpringAiTestController { @Resource private SpringAiTestService springAiTestService; // 流式输出接口(支持实时返回大模型响应) @GetMapping(value = "stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE) public Flux<String> stream(@RequestParam("content") String content) { return springAiTestService.stream(content); } }(2)Service:实现大模型调用逻辑定义服务接口及实现类,配置大模型连接信息并发起调用:// 服务接口 public interface SpringAiTestService { // 大模型流式输出方法 Flux<String> stream(String content); } // 服务实现类 import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil; import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatResponse; import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt; import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiChatModel; import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiChatOptions; import org.springframework.ai.openai.api.OpenAiApi; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; @Service public class SpringAiTestServiceImpl implements SpringAiTestService { @Override public Flux<String> stream(String content) { // 配置大模型平台(以硅基流动为例,兼容 OpenAI 接口格式) OpenAiChatModel chatModel = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .openAiApi(OpenAiApi.builder() .baseUrl("https://api.siliconflow.cn") // 硅基流动 API 地址 .apiKey(System.getenv("SiliconFlow_API")) // 从环境变量获取 API Key .build()) .defaultOptions(OpenAiChatOptions.builder() .model("Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507") // 指定模型 .build()) .build(); // 构建提问并发起流式调用 Prompt prompt = new Prompt(content); Flux<ChatResponse> stream = chatModel.stream(prompt); // 处理响应流,提取文本内容 return stream.map(chunk -> { String text = chunk.getResult() != null && chunk.getResult().getOutput() != null ? chunk.getResult().getOutput().getText() : ""; return StrUtil.nullToDefault(text, ""); // 避免 null 结果 }); } }3. 未集成 Tool 时的问题当我们调用接口提问 “今天是几号?” 时,大模型因无实时能力,回答明显不准确:这正是需要 Tool 工具方法的场景 —— 让大模型调用本地代码获取真实日期。二、核心实现:集成本地 Tool 工具方法通过 Spring AI 的 Tool 机制,让大模型在需要时自动调用本地代码(如获取当前日期),步骤如下:1. 创建本地 Tool 工具类定义一个获取当前日期的工具类,交给 Spring 管理(需实现 Function 接口):import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonClassDescription; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.function.Function; /** * 本地 Tool:获取当前日期 */ @Slf4j @Component("current_date") // 组件名称,用于后续指定 Tool public class CurrentDateToolFunction implements Function<CurrentDateToolFunction.Request, CurrentDateToolFunction.Response> { // 工具方法请求参数(无参数时为空类) @Data @JsonClassDescription("查询今天的日期") // 描述工具用途,帮助大模型理解 public static class Request { } // 工具方法响应结果 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public static class Response { private String date; // 日期结果(格式:yyyy-MM-dd) } // 核心逻辑:获取当前日期并返回 @Override public Response apply(Request request) { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); String currentDate = dateFormat.format(new Date()); log.info("调用本地 Tool 获取当前日期:{}", currentDate); return new Response(currentDate); } }关键说明:类上添加 @Component("current_date"),指定 Tool 名称为 current_date;Request 和 Response 类用于定义工具的输入输出格式,需配合 JSON 注解描述用途;apply 方法实现具体逻辑(此处为获取当前日期)。2. 修改大模型配置,启用 Tool在 Service 实现类中,为大模型配置 Tool 相关参数,使其能调用本地工具:@Override public Flux<String> stream(String content) { // 配置大模型,添加 Tool 支持 OpenAiChatModel chatModel = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .openAiApi(OpenAiApi.builder() .baseUrl("https://api.siliconflow.cn") .apiKey(System.getenv("SiliconFlow_API")) .build()) .defaultOptions(OpenAiChatOptions.builder() .model("Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507") .toolNames("current_date") // 指定启用的 Tool 名称(对应@Component的value) .build()) .toolCallingManager(SpringUtil.getBean(ToolCallingManager.class)) // 注入 Tool 调用管理器(Spring AI 提供) .build(); // 后续调用逻辑与之前一致... Prompt prompt = new Prompt(content); Flux<ChatResponse> stream = chatModel.stream(prompt); return stream.map(chunk -> { String text = chunk.getResult() != null && chunk.getResult().getOutput() != null ? chunk.getResult().getOutput().getText() : ""; return StrUtil.nullToDefault(text, ""); }); }核心配置:toolNames("current_date"):告诉大模型可调用名为 current_date 的 Tool;toolCallingManager:注入 Spring AI 提供的 ToolCallingManager,负责处理 Tool 调用流程。三、测试验证:Tool 工具调用效果再次调用接口提问 “今天是几号?”,大模型会自动触发 current_date 工具调用:1. 大模型响应结果大模型先说明 “将调用工具获取日期”,随后返回通过本地代码获取的准确日期。2. 本地日志验证查看应用日志,确认 Tool 被成功调用:2025-08-20 15:19:44.637 | INFO 28998 | boundedElastic-1 [TID: N/A] c.y.a.m.a.s.m.t.CurrentDateToolFunction | 调用本地 Tool 获取当前日期:2025-08-20总结通过本文案例,我们实现了 Spring AI 与本地 Tool 工具的集成,核心步骤可概括为:定义 Tool 工具类(实现 Function 接口,交给 Spring 管理);在大模型配置中指定 Tool 名称和调用管理器;大模型会根据提问自动判断是否调用 Tool,获取结果后整理回答。这种方式让大模型突破了自身局限,能灵活扩展实时数据获取、复杂计算等能力。下一篇将深入源码解析 Spring AI Tool 的底层实现原理,敬请期待! -
 Spring AI 无法获取大模型深度思考内容?解决方案来了 大模型的 “深度思考” 能力(即生成回答前的推理过程)正在成为提升交互体验的关键比如下面图中所看到的,Qwen 等模型会将推理过程放在reasoning_content字段中,让用户看到 “思考过程” 而非直接得到结果。但在 Java 开发中,使用 Spring AI 或 LangChain4J 等框架时,你可能会发现:这些框架会忽略reasoning_content字段,只返回最终回答。 这篇文章就来拆解这个问题的原因,并提供一套通过自定义接口调用实现 “获取完整思考过程” 的解决方案。问题:为什么框架无法获取深度思考内容?目前主流 Java 框架(Spring AI、LangChain4J)在设计时,默认只处理大模型的 “最终回答”(通常在content字段),而忽略了部分模型新增的 “思考过程” 字段(如reasoning_content)。具体表现为:字段被过滤:框架的响应解析逻辑中,没有处理reasoning_content的代码,导致这部分数据被直接丢弃。交互体验割裂:大模型的生成逻辑是 “先思考、后输出”,但框架会等待完整结果生成后才返回,用户需要长时间等待,且看不到中间思考过程。举个例子:当你调用 Qwen 模型时,原始接口返回会包含两部分内容:reasoning_content:“用户问我是谁,我需要先介绍自己的名字,再说明我的能力,还要保持友好的语气……”(思考过程)content:“我是通义千问,由通义实验室研发的超大规模语言模型。我能够帮助用户回答问题、创作文字,以及进行对话交流。如果你有任何问题或需要帮助,随时告诉我!”(最终回答)但通过 Spring AI 调用时,你只能拿到content部分,错失了展示 “思考过程” 的机会。解决方案:自定义接口调用,掌控原始数据既然框架的封装会丢失信息,那最直接的方案就是:绕过框架的限制,直接调用大模型的原生 API,获取完整响应数据。这种方式的优势在于:可获取所有字段(包括reasoning_content、usage等元数据);灵活控制流式输出逻辑,实现 “思考过程” 和 “最终回答” 的实时展示;便于业务扩展(如自定义缓存、日志、过滤规则等)。下面以 “调用硅基流动接口获取 Qwen 模型的思考过程” 为例,演示具体实现。实战:用 Spring WebFlux 调用硅基流动 API硅基流动是一个大模型聚合平台,支持 Qwen、GPT 等模型的调用,其 API 会返回完整的reasoning_content字段。我们用 Spring WebFlux(响应式 HTTP 客户端)实现调用,既能处理流式输出,又能获取原始响应。步骤 1:了解接口参数参考硅基流动官方 API 文档,核心请求参数如下:messages:对话历史(包含role和content);model:模型名称(如moonshotai/Kimi-Dev-72B);stream:是否开启流式输出(设为true,实时获取思考和回答);temperature:控制输出随机性(0-1 之间)。步骤 2:编码实现(获取完整响应)import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; public class SiliconFlowTest { // 硅基流动API地址 private static final String API_URL = "https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/chat/completions"; // 你的API Key(从硅基流动控制台获取) private static final String API_KEY = "your api-key"; private static final String NULL_MESSAGE = "null"; @Test public void testGetReasoningContent() { // 1. 构建请求体(包含对话和参数) String requestBody = """ { "messages": [ { "content": "你是一个聊天大师,请回答用户的问题。", "role": "system" }, { "content": "什么是Java响应式编程?", "role": "user" } ], "model": "Qwen/Qwen3-8B", "stream": true, "temperature": 0.7 } """; // 2. 用WebClient发送POST请求(响应式客户端) WebClient webClient = WebClient.create(API_URL); Flux<String> responseFlux = webClient.post() .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) .header("Authorization", "Bearer " + API_KEY) // 认证头 .bodyValue(requestBody) .retrieve() .bodyToFlux(String.class); // 流式接收原始响应 // 3. 处理响应(提取思考过程和最终回答) responseFlux.subscribe( // 每收到一段流式数据(SSE格式) chunk -> { // 解析原始响应(实际项目中建议用JSON工具解析) String reasoning = extractField(chunk, "reasoning_content"); String answer = extractField(chunk, "content"); if (!NULL_MESSAGE.equals(reasoning)) { System.out.println("[思考过程] " + reasoning); } if (!NULL_MESSAGE.equals(answer)) { System.out.println("[最终回答] " + answer); } }, // 错误处理 error -> System.err.println("请求错误:" + error.getMessage()), // 完成回调 () -> System.out.println("\n=== 输出结束 ===") ); // 阻塞等待(测试环境用,实际项目无需此代码) try { Thread.sleep(30000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 简易提取字段的工具方法(实际项目建议用Jackson/Gson解析) private String extractField(String chunk, String field) { String prefix = "\"" + field + "\":"; if (chunk.contains(prefix)) { String sub = chunk.split(prefix)[1].split(",\"")[0]; return sub.replace("\"", "").replace("\\n", "\n").trim(); } return ""; } }代码说明请求构建:通过 JSON 字符串定义对话和参数,重点开启stream: true以实时获取数据。响应处理:用Flux<String>接收流式响应(SSE 格式,每段是一个 JSON 片段);通过subscribe()回调实时解析reasoning_content(思考过程)和content(最终回答);实际项目中建议用 Jackson 等工具解析 JSON,替代示例中的简易字符串处理。核心价值:通过直接处理原始响应,同时获取 “思考过程” 和 “最终回答”,为前端展示(如分区域显示思考和回答)提供数据支持。业务扩展:如何在前端展示思考过程?获取到reasoning_content后,可通过以下方式提升用户体验:分区域展示:前端用两个容器,一个实时显示思考过程(灰色小字),一个显示最终回答(黑色大字)。格式标记:在后端给思考过程加上特殊标记(如<think>和</think>),前端解析时按标记区分:加载动画:在思考过程输出时,前端显示 “正在思考…” 的动画,降低用户等待焦虑。总结当 Spring AI 等框架无法满足 “获取大模型深度思考内容” 的需求时,直接调用原生 API 是最灵活的解决方案。通过 Spring WebFlux 处理流式响应,既能实时获取reasoning_content和content,又能保留扩展空间,轻松实现个性化业务逻辑。如果你需要更复杂的功能(如多模型切换、对话历史管理),可以在此基础上封装工具类,或结合响应式编程框架(如 Project Reactor)优化数据流处理。最后,附上两个链接:硅基流动 API 文档Spring WebFlux 响应式编程入门(我的另一篇博客)
Spring AI 无法获取大模型深度思考内容?解决方案来了 大模型的 “深度思考” 能力(即生成回答前的推理过程)正在成为提升交互体验的关键比如下面图中所看到的,Qwen 等模型会将推理过程放在reasoning_content字段中,让用户看到 “思考过程” 而非直接得到结果。但在 Java 开发中,使用 Spring AI 或 LangChain4J 等框架时,你可能会发现:这些框架会忽略reasoning_content字段,只返回最终回答。 这篇文章就来拆解这个问题的原因,并提供一套通过自定义接口调用实现 “获取完整思考过程” 的解决方案。问题:为什么框架无法获取深度思考内容?目前主流 Java 框架(Spring AI、LangChain4J)在设计时,默认只处理大模型的 “最终回答”(通常在content字段),而忽略了部分模型新增的 “思考过程” 字段(如reasoning_content)。具体表现为:字段被过滤:框架的响应解析逻辑中,没有处理reasoning_content的代码,导致这部分数据被直接丢弃。交互体验割裂:大模型的生成逻辑是 “先思考、后输出”,但框架会等待完整结果生成后才返回,用户需要长时间等待,且看不到中间思考过程。举个例子:当你调用 Qwen 模型时,原始接口返回会包含两部分内容:reasoning_content:“用户问我是谁,我需要先介绍自己的名字,再说明我的能力,还要保持友好的语气……”(思考过程)content:“我是通义千问,由通义实验室研发的超大规模语言模型。我能够帮助用户回答问题、创作文字,以及进行对话交流。如果你有任何问题或需要帮助,随时告诉我!”(最终回答)但通过 Spring AI 调用时,你只能拿到content部分,错失了展示 “思考过程” 的机会。解决方案:自定义接口调用,掌控原始数据既然框架的封装会丢失信息,那最直接的方案就是:绕过框架的限制,直接调用大模型的原生 API,获取完整响应数据。这种方式的优势在于:可获取所有字段(包括reasoning_content、usage等元数据);灵活控制流式输出逻辑,实现 “思考过程” 和 “最终回答” 的实时展示;便于业务扩展(如自定义缓存、日志、过滤规则等)。下面以 “调用硅基流动接口获取 Qwen 模型的思考过程” 为例,演示具体实现。实战:用 Spring WebFlux 调用硅基流动 API硅基流动是一个大模型聚合平台,支持 Qwen、GPT 等模型的调用,其 API 会返回完整的reasoning_content字段。我们用 Spring WebFlux(响应式 HTTP 客户端)实现调用,既能处理流式输出,又能获取原始响应。步骤 1:了解接口参数参考硅基流动官方 API 文档,核心请求参数如下:messages:对话历史(包含role和content);model:模型名称(如moonshotai/Kimi-Dev-72B);stream:是否开启流式输出(设为true,实时获取思考和回答);temperature:控制输出随机性(0-1 之间)。步骤 2:编码实现(获取完整响应)import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; public class SiliconFlowTest { // 硅基流动API地址 private static final String API_URL = "https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/chat/completions"; // 你的API Key(从硅基流动控制台获取) private static final String API_KEY = "your api-key"; private static final String NULL_MESSAGE = "null"; @Test public void testGetReasoningContent() { // 1. 构建请求体(包含对话和参数) String requestBody = """ { "messages": [ { "content": "你是一个聊天大师,请回答用户的问题。", "role": "system" }, { "content": "什么是Java响应式编程?", "role": "user" } ], "model": "Qwen/Qwen3-8B", "stream": true, "temperature": 0.7 } """; // 2. 用WebClient发送POST请求(响应式客户端) WebClient webClient = WebClient.create(API_URL); Flux<String> responseFlux = webClient.post() .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) .header("Authorization", "Bearer " + API_KEY) // 认证头 .bodyValue(requestBody) .retrieve() .bodyToFlux(String.class); // 流式接收原始响应 // 3. 处理响应(提取思考过程和最终回答) responseFlux.subscribe( // 每收到一段流式数据(SSE格式) chunk -> { // 解析原始响应(实际项目中建议用JSON工具解析) String reasoning = extractField(chunk, "reasoning_content"); String answer = extractField(chunk, "content"); if (!NULL_MESSAGE.equals(reasoning)) { System.out.println("[思考过程] " + reasoning); } if (!NULL_MESSAGE.equals(answer)) { System.out.println("[最终回答] " + answer); } }, // 错误处理 error -> System.err.println("请求错误:" + error.getMessage()), // 完成回调 () -> System.out.println("\n=== 输出结束 ===") ); // 阻塞等待(测试环境用,实际项目无需此代码) try { Thread.sleep(30000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 简易提取字段的工具方法(实际项目建议用Jackson/Gson解析) private String extractField(String chunk, String field) { String prefix = "\"" + field + "\":"; if (chunk.contains(prefix)) { String sub = chunk.split(prefix)[1].split(",\"")[0]; return sub.replace("\"", "").replace("\\n", "\n").trim(); } return ""; } }代码说明请求构建:通过 JSON 字符串定义对话和参数,重点开启stream: true以实时获取数据。响应处理:用Flux<String>接收流式响应(SSE 格式,每段是一个 JSON 片段);通过subscribe()回调实时解析reasoning_content(思考过程)和content(最终回答);实际项目中建议用 Jackson 等工具解析 JSON,替代示例中的简易字符串处理。核心价值:通过直接处理原始响应,同时获取 “思考过程” 和 “最终回答”,为前端展示(如分区域显示思考和回答)提供数据支持。业务扩展:如何在前端展示思考过程?获取到reasoning_content后,可通过以下方式提升用户体验:分区域展示:前端用两个容器,一个实时显示思考过程(灰色小字),一个显示最终回答(黑色大字)。格式标记:在后端给思考过程加上特殊标记(如<think>和</think>),前端解析时按标记区分:加载动画:在思考过程输出时,前端显示 “正在思考…” 的动画,降低用户等待焦虑。总结当 Spring AI 等框架无法满足 “获取大模型深度思考内容” 的需求时,直接调用原生 API 是最灵活的解决方案。通过 Spring WebFlux 处理流式响应,既能实时获取reasoning_content和content,又能保留扩展空间,轻松实现个性化业务逻辑。如果你需要更复杂的功能(如多模型切换、对话历史管理),可以在此基础上封装工具类,或结合响应式编程框架(如 Project Reactor)优化数据流处理。最后,附上两个链接:硅基流动 API 文档Spring WebFlux 响应式编程入门(我的另一篇博客) -
 在 Ubuntu 环境下安装与配置 Nginx 的完整指南 Nginx简介 Nginx是一款高性能的开源 Web 服务器、反向代理服务器、负载均衡器和 HTTP 缓存工具。它由俄罗斯程序员伊戈尔・赛索耶夫(Igor Sysoev)于 2004 年首次公开发布,最初设计的目标是解决高并发场景下的性能瓶颈,如今已成为全球最流行的服务器软件之一,被 Netflix、Airbnb、GitHub、腾讯、阿里等众多大型企业广泛使用。本文将详细介绍如何在 Ubuntu 系统中安装、配置并优化 Nginx,适合初学者入门参考。一、安装 NginxUbuntu 的官方软件仓库中已经包含了 Nginx,我们可以通过 APT 包管理器轻松安装。更新系统包列表首先确保系统包列表是最新的:sudo apt update安装 Nginx执行以下命令安装 Nginx:sudo apt install nginx验证安装是否成功安装完成后,Nginx 会自动启动。可以通过以下命令检查其运行状态:sudo systemctl status nginx如果看到 "active (running)" 字样,说明 Nginx 已经成功启动。配置防火墙 4.1 如果你的 Ubuntu 系统启用了 UFW 防火墙,需要允许 HTTP(80 端口)和 HTTPS(443 端口)流量:sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'可以通过以下命令验证防火墙规则:sudo ufw status 4.2 如果你跟我一样,使用的是云服务器,那么只需要在安全组中开放80端口即可二、Nginx的基本操作掌握以下基本命令可以帮助你管理 Nginx 服务:启动 Nginx:sudo systemctl start nginx停止 Nginx:sudo systemctl stop nginx重启 Nginx:sudo systemctl restart nginx重新加载配置(不中断服务):sudo systemctl reload nginx设置开机自启动:sudo systemctl enable nginx禁止开机自启动:sudo systemctl disable nginx三、Nginx 的配置文件结构Nginx 的配置文件位于/etc/nginx目录下,主要文件和目录包括:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:主配置文件/etc/nginx/sites-available/:存储所有网站的配置文件/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/:存储启用的网站配置(通常是指向 sites-available 目录的软链接)/etc/nginx/conf.d/:可以存放额外的配置片段/etc/nginx/mime.types:定义 MIME 类型这种结构允许我们为每个网站创建独立的配置文件,便于管理。四、配置一个基本的 Web 站点下面我们创建一个简单的 Web 站点配置:创建网站目录首先为网站创建一个目录,并设置适当的权限:sudo mkdir -p /var/www/example.com/html sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/example.com/html sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www创建测试页面在网站目录下创建一个简单的 HTML 文件:nano /var/www/example.com/html/index.html添加以下内容:预览 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to Example.com!</title> </head> <body> <h1>Success! The example.com server block is working!</h1> </body> </html>保存并关闭文件。创建服务器配置文件在sites-available目录下创建一个新的配置文件:sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com添加以下配置:server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; root /var/www/example.com/html; index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name example.com www.example.com; # 替换为你的域名或服务器 IP(如 1.2.3.4) location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }这个配置指定了:监听 80 端口(HTTP)网站文件根目录默认索引文件服务器域名基本的请求处理规则启用站点配置通过创建软链接将配置文件链接到sites-enabled目录:sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/检查配置文件语法在应用配置之前,先检查语法是否正确:sudo nginx -t如果输出 "nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful",说明配置没有问题。重新加载 Nginx使配置生效:sudo systemctl reload nginx测试网站如果你的域名已经解析到服务器 IP,现在可以通过浏览器访问http://example.com来查看效果。如果没有域名,可以修改本地hosts文件进行测试。五、注意如果访问80端口,显示Apache2默认页面,说明80端口被Apache服务器占用了,可以通过一下命令停止Apache服务器sudo systemctl stop apache2再次访问就可以成功访问到我们部署的页面了
在 Ubuntu 环境下安装与配置 Nginx 的完整指南 Nginx简介 Nginx是一款高性能的开源 Web 服务器、反向代理服务器、负载均衡器和 HTTP 缓存工具。它由俄罗斯程序员伊戈尔・赛索耶夫(Igor Sysoev)于 2004 年首次公开发布,最初设计的目标是解决高并发场景下的性能瓶颈,如今已成为全球最流行的服务器软件之一,被 Netflix、Airbnb、GitHub、腾讯、阿里等众多大型企业广泛使用。本文将详细介绍如何在 Ubuntu 系统中安装、配置并优化 Nginx,适合初学者入门参考。一、安装 NginxUbuntu 的官方软件仓库中已经包含了 Nginx,我们可以通过 APT 包管理器轻松安装。更新系统包列表首先确保系统包列表是最新的:sudo apt update安装 Nginx执行以下命令安装 Nginx:sudo apt install nginx验证安装是否成功安装完成后,Nginx 会自动启动。可以通过以下命令检查其运行状态:sudo systemctl status nginx如果看到 "active (running)" 字样,说明 Nginx 已经成功启动。配置防火墙 4.1 如果你的 Ubuntu 系统启用了 UFW 防火墙,需要允许 HTTP(80 端口)和 HTTPS(443 端口)流量:sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'可以通过以下命令验证防火墙规则:sudo ufw status 4.2 如果你跟我一样,使用的是云服务器,那么只需要在安全组中开放80端口即可二、Nginx的基本操作掌握以下基本命令可以帮助你管理 Nginx 服务:启动 Nginx:sudo systemctl start nginx停止 Nginx:sudo systemctl stop nginx重启 Nginx:sudo systemctl restart nginx重新加载配置(不中断服务):sudo systemctl reload nginx设置开机自启动:sudo systemctl enable nginx禁止开机自启动:sudo systemctl disable nginx三、Nginx 的配置文件结构Nginx 的配置文件位于/etc/nginx目录下,主要文件和目录包括:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:主配置文件/etc/nginx/sites-available/:存储所有网站的配置文件/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/:存储启用的网站配置(通常是指向 sites-available 目录的软链接)/etc/nginx/conf.d/:可以存放额外的配置片段/etc/nginx/mime.types:定义 MIME 类型这种结构允许我们为每个网站创建独立的配置文件,便于管理。四、配置一个基本的 Web 站点下面我们创建一个简单的 Web 站点配置:创建网站目录首先为网站创建一个目录,并设置适当的权限:sudo mkdir -p /var/www/example.com/html sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/example.com/html sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www创建测试页面在网站目录下创建一个简单的 HTML 文件:nano /var/www/example.com/html/index.html添加以下内容:预览 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to Example.com!</title> </head> <body> <h1>Success! The example.com server block is working!</h1> </body> </html>保存并关闭文件。创建服务器配置文件在sites-available目录下创建一个新的配置文件:sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com添加以下配置:server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; root /var/www/example.com/html; index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name example.com www.example.com; # 替换为你的域名或服务器 IP(如 1.2.3.4) location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }这个配置指定了:监听 80 端口(HTTP)网站文件根目录默认索引文件服务器域名基本的请求处理规则启用站点配置通过创建软链接将配置文件链接到sites-enabled目录:sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/检查配置文件语法在应用配置之前,先检查语法是否正确:sudo nginx -t如果输出 "nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful",说明配置没有问题。重新加载 Nginx使配置生效:sudo systemctl reload nginx测试网站如果你的域名已经解析到服务器 IP,现在可以通过浏览器访问http://example.com来查看效果。如果没有域名,可以修改本地hosts文件进行测试。五、注意如果访问80端口,显示Apache2默认页面,说明80端口被Apache服务器占用了,可以通过一下命令停止Apache服务器sudo systemctl stop apache2再次访问就可以成功访问到我们部署的页面了 -
 自定义 Spring-Boot-Starter 结合 TrueLicense 实现证书授权拦截 引言在软件产品交付场景中,授权管理是保障软件权益的重要手段。传统的硬编码时间限制方式存在修改麻烦、需重新部署等问题,而基于证书(License)的授权方式可通过替换证书文件实现灵活授权,无需改动源码。本文将详解如何基于 Spring Boot 自定义 Starter,并整合开源证书管理引擎 TrueLicense,实现对接口的证书授权拦截功能,帮助开发者快速搭建可控的授权体系。一、技术背景与场景说明1.1 什么是 TrueLicense?TrueLicense 是一个基于 Java 的开源证书管理引擎,提供了证书的生成、颁发、验证等核心功能,支持通过密钥对加密证书内容,确保授权信息的安全性。其官网地址为:https://truelicense.java.net。1.2 为什么需要自定义 Spring Boot Starter?Spring Boot Starter 的核心作用是简化依赖管理和自动配置。通过自定义 Starter,我们可以将证书校验逻辑封装为独立组件,只需在目标项目中引入依赖并配置参数,即可快速集成证书授权功能,实现 "即插即用"。1.3 核心场景软件试用期授权:通过证书指定有效期,到期后自动限制使用。硬件绑定授权:限制软件仅能在指定 MAC 地址的设备上运行。接口级授权控制:对敏感接口添加证书校验,未授权请求直接拦截。二、密钥对生成(基于 keytool)证书的安全性依赖于非对称加密的密钥对(私钥用于生成证书,公钥用于验证证书)。我们使用 JDK 自带的keytool工具生成密钥对,步骤如下:2.1 生成私钥库私钥库用于存储生成证书的私钥,执行以下命令:keytool -genkey -alias privatekey -keystore privateKeys.store -storepass "123456q" -keypass "123456q" -keysize 1024 -validity 3650参数说明:-alias privatekey:私钥别名(后续生成证书需引用)。-keystore privateKeys.store:生成的私钥库文件名。-storepass "123456q":私钥库访问密码。-keypass "123456q":私钥本身的密码(建议与 storepass 一致,简化管理)。-keysize 1024:密钥长度(1024 位及以上确保安全性)。-validity 3650:私钥有效期(单位:天,此处为 10 年)。执行后需输入所有者信息(如姓名、组织等),可根据实际情况填写。2.2 导出公钥证书从私钥库中导出公钥证书(用于校验证书的合法性):keytool -export -alias privatekey -file certfile.cer -keystore privateKeys.store -storepass "123456q"参数说明:-export:指定操作类型为导出证书。-file certfile.cer:导出的公钥证书文件名。执行成功后,当前目录会生成certfile.cer公钥文件。2.3 导入公钥到公钥库将公钥证书导入公钥库(供应用程序验证证书时使用):keytool -import -alias publiccert -file certfile.cer -keystore publicCerts.store -storepass "123456q"参数说明:-alias publiccert:公钥在公钥库中的别名(后续校验需引用)。-keystore publicCerts.store:生成的公钥库文件名。执行时需确认导入(输入yes),完成后公钥库publicCerts.store生成。注意:私钥库(privateKeys.store)需妥善保管,公钥库(publicCerts.store)和公钥证书(certfile.cer)可随应用程序部署。三、证书生成工具实现基于 TrueLicense 的 API,我们可以通过代码生成证书文件。以下是核心实现步骤:3.1 核心参数类定义首先定义证书生成所需的参数封装类(LicenseCreatorParam):/** * License证书生成类需要的参数 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseCreatorParam implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 2832129012982731724L; /** * 证书subject * */ private String subject; /** * 密钥级别 * */ private String privateAlias; /** * 密钥密码(需要妥善保存,密钥不能让使用者知道) */ private String keyPass; /** * 访问密钥库的密码 * */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 * */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 * */ private String privateKeysStorePath; /** * 证书生效时间 * */ @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8") private Date issuedTime = new Date(); /** * 证书的失效时间 * */ @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8") private Date expiryTime; /** * 用户的使用类型 * */ private String consumerType ="user"; /** * 用户使用数量 * */ private Integer consumerAmount = 1; /** * 描述信息 * */ private String description = ""; /** * 额外的服务器硬件校验信息(机器码) * */ private LicenseCheckModel licenseCheckModel; }/** * 自定义需要校验的参数 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseCheckModel implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2314678441082223148L; /** * 可被允许IP地址白名单 * */ private List<String> ipAddress; /** * 可被允许的MAC地址白名单(网络设备接口的物理地址,通常固化在网卡(Network Interface Card,NIC)的EEPROM(电可擦可编程只读存储器)中,具有全球唯一性。) * */ private List<String> macAddress; /** * 可允许的CPU序列号 * */ private String cpuSerial; /** * 可允许的主板序列号(硬件序列化?) * */ private String mainBoardSerial; }3.2 证书生成器实现实现LicenseCreator类,封装证书生成逻辑:public class LicenseCreator { private final static X500Principal DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER = new X500Principal("CN=localhost, OU=localhost, O=localhost, L=SH, ST=SH, C=CN"); private final LicenseCreatorParam param; public LicenseCreator(LicenseCreatorParam param) { this.param = param; } /** * 生成License证书 * @return boolean */ public boolean generateLicense(){ try { LicenseManager licenseManager = new CustomLicenseManager(initLicenseParam()); LicenseContent licenseContent = initLicenseContent(); licenseManager.store(licenseContent,new File(param.getLicensePath())); return true; }catch (Exception e){ throw new LicenseCreateException(MessageFormat.format("证书生成失败:{0}", param), e); } } /** * 初始化证书生成参数 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseParam */ private LicenseParam initLicenseParam(){ Preferences preferences = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(LicenseCreator.class); //设置对证书内容加密的秘钥 CipherParam cipherParam = new DefaultCipherParam(param.getStorePass()); KeyStoreParam privateStoreParam = new CustomKeyStoreParam(LicenseCreator.class ,param.getPrivateKeysStorePath() ,param.getPrivateAlias() ,param.getStorePass() ,param.getKeyPass()); return new DefaultLicenseParam(param.getSubject() ,preferences ,privateStoreParam ,cipherParam); } /** * 设置证书生成正文信息 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseContent */ private LicenseContent initLicenseContent(){ LicenseContent licenseContent = new LicenseContent(); licenseContent.setHolder(DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER); licenseContent.setIssuer(DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER); licenseContent.setSubject(param.getSubject()); licenseContent.setIssued(param.getIssuedTime()); licenseContent.setNotBefore(param.getIssuedTime()); licenseContent.setNotAfter(param.getExpiryTime()); licenseContent.setConsumerType(param.getConsumerType()); licenseContent.setConsumerAmount(param.getConsumerAmount()); licenseContent.setInfo(param.getDescription()); //扩展校验服务器硬件信息 licenseContent.setExtra(param.getLicenseCheckModel()); return licenseContent; } }3.3 生成证书示例通过单元测试或主方法生成证书:public class LicenseCreateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { LicenseCreatorParam param = new LicenseCreatorParam(); param.setSubject("your subject"); param.setPrivateAlias("privatekey"); // 与私钥库中别名一致 param.setKeyPass("123456q"); // 私钥密码 param.setStorePass("123456q"); // 私钥库密码 param.setLicensePath("your path"); // 证书输出路径 param.setPrivateKeysStorePath("your path"); // 私钥库路径 param.setIssuedTime(DateUtil.parseDate("2025-05-25")); // 生效时间 param.setExpiryTime(DateUtil.parseDate("2025-09-01")); // 过期时间 param.setConsumerType("your type"); param.setConsumerAmount(1); param.setDescription("your desc"); // 绑定MAC地址(仅允许指定设备使用) LicenseCheckModel checkModel = new LicenseCheckModel(); checkModel.setMacAddressList(Collections.singletonList("8c:84:74:e7:62:a6")); param.setLicenseCheckModel(checkModel); // 生成证书 LicenseCreator creator = new LicenseCreator(param); boolean result = creator.generateLicense(); System.out.println("证书生成结果:" + (result ? "成功" : "失败")); } }执行后,指定路径会生成your path.lic证书文件。四、证书校验核心逻辑应用程序需通过公钥库验证证书的合法性(有效期、设备绑定等),核心实现如下:4.1 校验参数类定义/** * license证书校验参数类 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseVerifyParam { /** * 证书subject */ private String subject; /** * 公钥别称 */ private String publicAlias; /** * 访问公钥库的密码 */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 */ private String publicKeysStorePath; }4.2 校验器实现/** * license证书校验类 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Slf4j public class LicenseVerify { /** * 认证需要提供的参数 */ private final LicenseVerifyParam param; /** * 是否启用license */ private final Boolean enableLicense; public LicenseVerify(LicenseVerifyParam param,Boolean enableLicense) { this.param = param; this.enableLicense = enableLicense; } /** * 安装License证书 */ public synchronized LicenseContent install(){ log.info("服务启动,检查是否启用license验证,结果:" + enableLicense); if (!enableLicense) { return null; } LicenseContent result = null; DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //1. 安装证书 try{ LicenseManager licenseManager = LicenseManagerHolder.getInstance(initLicenseParam(param)); licenseManager.uninstall(); result = licenseManager.install(new File(param.getLicensePath())); log.info(MessageFormat.format("证书安装成功,证书有效期:{0} - {1}",format.format(result.getNotBefore()),format.format(result.getNotAfter()))); }catch (Exception e){ log.error("证书安装失败!",e); } return result; } /** * 校验License证书 * @return boolean */ public boolean verify(){ LicenseManager licenseManager = LicenseManagerHolder.getInstance(null); DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //2. 校验证书 try { LicenseContent licenseContent = licenseManager.verify(); log.info(MessageFormat.format("证书校验通过,证书有效期:{0} - {1}",format.format(licenseContent.getNotBefore()),format.format(licenseContent.getNotAfter()))); return true; }catch (Exception e){ log.error("证书校验失败!",e); return false; } } /** * 初始化证书生成参数 * @param param License校验类需要的参数 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseParam */ private LicenseParam initLicenseParam(LicenseVerifyParam param){ Preferences preferences = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(LicenseVerify.class); CipherParam cipherParam = new DefaultCipherParam(param.getStorePass()); KeyStoreParam publicStoreParam = new CustomKeyStoreParam(LicenseVerify.class ,param.getPublicKeysStorePath() ,param.getPublicAlias() ,param.getStorePass() ,null); return new DefaultLicenseParam(param.getSubject() ,preferences ,publicStoreParam ,cipherParam); } } 五、Spring Boot Starter 自动配置5.1 配置属性类定义配置文件参数映射类,支持通过application.yml配置证书相关参数:/** * 证书认证属性类 * * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "license") public class LicenseConfigProperties { /** * 证书subject */ private String subject; /** * 公钥别称 */ private String publicAlias; /** * 访问公钥库的密码 */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 */ private String publicKeysStorePath; /** * 是否启用license认证 */ private Boolean enableLicense; }5.2 自动配置类通过@Configuration实现自动配置,注入校验器 Bean:@Configuration @AllArgsConstructor @EnableConfigurationProperties(LicenseConfigProperties.class) public class LicenseAutoConfiguration { private final LicenseConfigProperties licenseConfigProperties; // 注入LicenseVerify Bean,启动时执行install方法 @Bean(initMethod = "install") public LicenseVerify licenseVerify() { LicenseVerifyParam param = new LicenseVerifyParam(); param.setSubject(licenseConfigProperties.getSubject()); param.setPublicAlias(licenseConfigProperties.getPublicAlias()); param.setStorePass(licenseConfigProperties.getStorePass()); param.setLicensePath(licenseConfigProperties.getLicensePath()); param.setPublicKeysStorePath(licenseConfigProperties.getPublicKeysStorePath()); return new LicenseVerify(param, licenseConfigProperties.getEnableLicense()); } }5.3 AOP 拦截实现通过自定义注解@RequireLicense和 AOP 拦截,实现接口级别的证书校验:5.3.1 自定义注解/** * 标记需要证书校验的接口方法 */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RequireLicense { boolean value() default true; // 是否启用校验(默认启用) }5.3.2 AOP 拦截逻辑@Slf4j @Aspect @Component public class RequireLicenseAspect { private final LicenseVerify licenseVerify; private final LicenseConfigProperties properties; public RequireLicenseAspect(LicenseVerify licenseVerify, LicenseConfigProperties properties) { this.licenseVerify = licenseVerify; this.properties = properties; } // 拦截所有添加@RequireLicense注解的方法 @Around("@annotation(requireLicense)") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point, RequireLicense requireLicense) throws Throwable { // 注解禁用校验或全局禁用校验,直接执行方法 if (!requireLicense.value() || !properties.getEnableLicense()) { log.info("接口[{}]跳过证书校验", point.getSignature().getName()); return point.proceed(); } // 执行证书校验 boolean verifyResult = licenseVerify.verify(); if (verifyResult) { return point.proceed(); // 校验通过,执行原方法 } else { throw new LicenseInterceptException("接口调用失败:证书未授权或已过期"); } } }5.4 注册自动配置类在src/main/resources/META-INF目录下创建spring.factories文件,指定自动配置类:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ com.jcq.license.autoconfigure.LicenseAutoConfiguration,\ com.jcq.license.verify.aop.RequireLicenseAspect六、Starter 打包配置为确保其他项目引用 Starter 时能正常加载类,需修改pom.xml的构建配置:<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <!-- 跳过Spring Boot默认的可执行JAR打包(避免类路径嵌套在BOOT-INF下) --> <configuration> <skip>true</skip> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>原因:默认情况下,Spring Boot 插件会将类打包到BOOT-INF/classes目录下,导致其他项目引用时无法通过常规类路径加载类。设置skip=true后,会生成标准的 JAR 包,类路径更友好。七、使用示例7.1 引入依赖在目标项目的pom.xml中引入自定义 Starter:<dependency> <groupId>com.jcq</groupId> <artifactId>license-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>7.2 配置参数在application.yml中配置证书相关参数,配置时idea会弹出提示:license: subject: 企业版软件授权证书 public-alias: publiccert store-pass: 123456q license-path: classpath:license.lic # 证书文件存放路径 public-keys-store-path: classpath:publicCerts.store # 公钥库路径 enable-license: true # 启用证书校验7.3 接口使用注解在需要授权的接口方法上添加@RequireLicense注解:@RestController @RequestMapping("/api") public class DemoController { @GetMapping("/sensitive") @RequireLicense // 需要证书校验 public String sensitiveOperation() { return "敏感操作执行成功(已授权)"; } @GetMapping("/public") @RequireLicense(false) // 禁用校验(即使全局启用也会跳过) public String publicOperation() { return "公开操作执行成功(无需授权)"; } }八、总结本文通过自定义 Spring Boot Starter 整合 TrueLicense,实现了一套灵活的证书授权方案,核心优势包括:可插拔性:通过 Starter 封装,引入依赖即可使用,无需重复开发。灵活性:支持全局开关和接口级开关,方便测试环境跳过校验。安全性:基于非对称加密和硬件绑定,防止证书伪造和非法传播。易维护:授权到期后只需替换证书文件,无需修改代码或重启服务。实际项目中可根据需求扩展校验维度(如 CPU 序列号、内存大小等),进一步增强授权的安全性。附录:核心类说明类名作用LicenseCreator证书生成工具类LicenseVerify证书校验核心类(启动校验 + 实时校验)LicenseConfigProperties配置参数映射类LicenseAutoConfigurationStarter 自动配置类RequireLicense接口校验注解RequireLicenseAspectAOP 拦截器(实现接口级校验)完整源码可参考 GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/Jucunqi/license-spring-boot-starter.git(示例地址)。
自定义 Spring-Boot-Starter 结合 TrueLicense 实现证书授权拦截 引言在软件产品交付场景中,授权管理是保障软件权益的重要手段。传统的硬编码时间限制方式存在修改麻烦、需重新部署等问题,而基于证书(License)的授权方式可通过替换证书文件实现灵活授权,无需改动源码。本文将详解如何基于 Spring Boot 自定义 Starter,并整合开源证书管理引擎 TrueLicense,实现对接口的证书授权拦截功能,帮助开发者快速搭建可控的授权体系。一、技术背景与场景说明1.1 什么是 TrueLicense?TrueLicense 是一个基于 Java 的开源证书管理引擎,提供了证书的生成、颁发、验证等核心功能,支持通过密钥对加密证书内容,确保授权信息的安全性。其官网地址为:https://truelicense.java.net。1.2 为什么需要自定义 Spring Boot Starter?Spring Boot Starter 的核心作用是简化依赖管理和自动配置。通过自定义 Starter,我们可以将证书校验逻辑封装为独立组件,只需在目标项目中引入依赖并配置参数,即可快速集成证书授权功能,实现 "即插即用"。1.3 核心场景软件试用期授权:通过证书指定有效期,到期后自动限制使用。硬件绑定授权:限制软件仅能在指定 MAC 地址的设备上运行。接口级授权控制:对敏感接口添加证书校验,未授权请求直接拦截。二、密钥对生成(基于 keytool)证书的安全性依赖于非对称加密的密钥对(私钥用于生成证书,公钥用于验证证书)。我们使用 JDK 自带的keytool工具生成密钥对,步骤如下:2.1 生成私钥库私钥库用于存储生成证书的私钥,执行以下命令:keytool -genkey -alias privatekey -keystore privateKeys.store -storepass "123456q" -keypass "123456q" -keysize 1024 -validity 3650参数说明:-alias privatekey:私钥别名(后续生成证书需引用)。-keystore privateKeys.store:生成的私钥库文件名。-storepass "123456q":私钥库访问密码。-keypass "123456q":私钥本身的密码(建议与 storepass 一致,简化管理)。-keysize 1024:密钥长度(1024 位及以上确保安全性)。-validity 3650:私钥有效期(单位:天,此处为 10 年)。执行后需输入所有者信息(如姓名、组织等),可根据实际情况填写。2.2 导出公钥证书从私钥库中导出公钥证书(用于校验证书的合法性):keytool -export -alias privatekey -file certfile.cer -keystore privateKeys.store -storepass "123456q"参数说明:-export:指定操作类型为导出证书。-file certfile.cer:导出的公钥证书文件名。执行成功后,当前目录会生成certfile.cer公钥文件。2.3 导入公钥到公钥库将公钥证书导入公钥库(供应用程序验证证书时使用):keytool -import -alias publiccert -file certfile.cer -keystore publicCerts.store -storepass "123456q"参数说明:-alias publiccert:公钥在公钥库中的别名(后续校验需引用)。-keystore publicCerts.store:生成的公钥库文件名。执行时需确认导入(输入yes),完成后公钥库publicCerts.store生成。注意:私钥库(privateKeys.store)需妥善保管,公钥库(publicCerts.store)和公钥证书(certfile.cer)可随应用程序部署。三、证书生成工具实现基于 TrueLicense 的 API,我们可以通过代码生成证书文件。以下是核心实现步骤:3.1 核心参数类定义首先定义证书生成所需的参数封装类(LicenseCreatorParam):/** * License证书生成类需要的参数 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseCreatorParam implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 2832129012982731724L; /** * 证书subject * */ private String subject; /** * 密钥级别 * */ private String privateAlias; /** * 密钥密码(需要妥善保存,密钥不能让使用者知道) */ private String keyPass; /** * 访问密钥库的密码 * */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 * */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 * */ private String privateKeysStorePath; /** * 证书生效时间 * */ @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8") private Date issuedTime = new Date(); /** * 证书的失效时间 * */ @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8") private Date expiryTime; /** * 用户的使用类型 * */ private String consumerType ="user"; /** * 用户使用数量 * */ private Integer consumerAmount = 1; /** * 描述信息 * */ private String description = ""; /** * 额外的服务器硬件校验信息(机器码) * */ private LicenseCheckModel licenseCheckModel; }/** * 自定义需要校验的参数 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseCheckModel implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2314678441082223148L; /** * 可被允许IP地址白名单 * */ private List<String> ipAddress; /** * 可被允许的MAC地址白名单(网络设备接口的物理地址,通常固化在网卡(Network Interface Card,NIC)的EEPROM(电可擦可编程只读存储器)中,具有全球唯一性。) * */ private List<String> macAddress; /** * 可允许的CPU序列号 * */ private String cpuSerial; /** * 可允许的主板序列号(硬件序列化?) * */ private String mainBoardSerial; }3.2 证书生成器实现实现LicenseCreator类,封装证书生成逻辑:public class LicenseCreator { private final static X500Principal DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER = new X500Principal("CN=localhost, OU=localhost, O=localhost, L=SH, ST=SH, C=CN"); private final LicenseCreatorParam param; public LicenseCreator(LicenseCreatorParam param) { this.param = param; } /** * 生成License证书 * @return boolean */ public boolean generateLicense(){ try { LicenseManager licenseManager = new CustomLicenseManager(initLicenseParam()); LicenseContent licenseContent = initLicenseContent(); licenseManager.store(licenseContent,new File(param.getLicensePath())); return true; }catch (Exception e){ throw new LicenseCreateException(MessageFormat.format("证书生成失败:{0}", param), e); } } /** * 初始化证书生成参数 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseParam */ private LicenseParam initLicenseParam(){ Preferences preferences = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(LicenseCreator.class); //设置对证书内容加密的秘钥 CipherParam cipherParam = new DefaultCipherParam(param.getStorePass()); KeyStoreParam privateStoreParam = new CustomKeyStoreParam(LicenseCreator.class ,param.getPrivateKeysStorePath() ,param.getPrivateAlias() ,param.getStorePass() ,param.getKeyPass()); return new DefaultLicenseParam(param.getSubject() ,preferences ,privateStoreParam ,cipherParam); } /** * 设置证书生成正文信息 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseContent */ private LicenseContent initLicenseContent(){ LicenseContent licenseContent = new LicenseContent(); licenseContent.setHolder(DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER); licenseContent.setIssuer(DEFAULT_HOLDER_AND_ISSUER); licenseContent.setSubject(param.getSubject()); licenseContent.setIssued(param.getIssuedTime()); licenseContent.setNotBefore(param.getIssuedTime()); licenseContent.setNotAfter(param.getExpiryTime()); licenseContent.setConsumerType(param.getConsumerType()); licenseContent.setConsumerAmount(param.getConsumerAmount()); licenseContent.setInfo(param.getDescription()); //扩展校验服务器硬件信息 licenseContent.setExtra(param.getLicenseCheckModel()); return licenseContent; } }3.3 生成证书示例通过单元测试或主方法生成证书:public class LicenseCreateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { LicenseCreatorParam param = new LicenseCreatorParam(); param.setSubject("your subject"); param.setPrivateAlias("privatekey"); // 与私钥库中别名一致 param.setKeyPass("123456q"); // 私钥密码 param.setStorePass("123456q"); // 私钥库密码 param.setLicensePath("your path"); // 证书输出路径 param.setPrivateKeysStorePath("your path"); // 私钥库路径 param.setIssuedTime(DateUtil.parseDate("2025-05-25")); // 生效时间 param.setExpiryTime(DateUtil.parseDate("2025-09-01")); // 过期时间 param.setConsumerType("your type"); param.setConsumerAmount(1); param.setDescription("your desc"); // 绑定MAC地址(仅允许指定设备使用) LicenseCheckModel checkModel = new LicenseCheckModel(); checkModel.setMacAddressList(Collections.singletonList("8c:84:74:e7:62:a6")); param.setLicenseCheckModel(checkModel); // 生成证书 LicenseCreator creator = new LicenseCreator(param); boolean result = creator.generateLicense(); System.out.println("证书生成结果:" + (result ? "成功" : "失败")); } }执行后,指定路径会生成your path.lic证书文件。四、证书校验核心逻辑应用程序需通过公钥库验证证书的合法性(有效期、设备绑定等),核心实现如下:4.1 校验参数类定义/** * license证书校验参数类 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data public class LicenseVerifyParam { /** * 证书subject */ private String subject; /** * 公钥别称 */ private String publicAlias; /** * 访问公钥库的密码 */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 */ private String publicKeysStorePath; }4.2 校验器实现/** * license证书校验类 * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Slf4j public class LicenseVerify { /** * 认证需要提供的参数 */ private final LicenseVerifyParam param; /** * 是否启用license */ private final Boolean enableLicense; public LicenseVerify(LicenseVerifyParam param,Boolean enableLicense) { this.param = param; this.enableLicense = enableLicense; } /** * 安装License证书 */ public synchronized LicenseContent install(){ log.info("服务启动,检查是否启用license验证,结果:" + enableLicense); if (!enableLicense) { return null; } LicenseContent result = null; DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //1. 安装证书 try{ LicenseManager licenseManager = LicenseManagerHolder.getInstance(initLicenseParam(param)); licenseManager.uninstall(); result = licenseManager.install(new File(param.getLicensePath())); log.info(MessageFormat.format("证书安装成功,证书有效期:{0} - {1}",format.format(result.getNotBefore()),format.format(result.getNotAfter()))); }catch (Exception e){ log.error("证书安装失败!",e); } return result; } /** * 校验License证书 * @return boolean */ public boolean verify(){ LicenseManager licenseManager = LicenseManagerHolder.getInstance(null); DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //2. 校验证书 try { LicenseContent licenseContent = licenseManager.verify(); log.info(MessageFormat.format("证书校验通过,证书有效期:{0} - {1}",format.format(licenseContent.getNotBefore()),format.format(licenseContent.getNotAfter()))); return true; }catch (Exception e){ log.error("证书校验失败!",e); return false; } } /** * 初始化证书生成参数 * @param param License校验类需要的参数 * @return de.schlichtherle.license.LicenseParam */ private LicenseParam initLicenseParam(LicenseVerifyParam param){ Preferences preferences = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(LicenseVerify.class); CipherParam cipherParam = new DefaultCipherParam(param.getStorePass()); KeyStoreParam publicStoreParam = new CustomKeyStoreParam(LicenseVerify.class ,param.getPublicKeysStorePath() ,param.getPublicAlias() ,param.getStorePass() ,null); return new DefaultLicenseParam(param.getSubject() ,preferences ,publicStoreParam ,cipherParam); } } 五、Spring Boot Starter 自动配置5.1 配置属性类定义配置文件参数映射类,支持通过application.yml配置证书相关参数:/** * 证书认证属性类 * * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/3/12 */ @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "license") public class LicenseConfigProperties { /** * 证书subject */ private String subject; /** * 公钥别称 */ private String publicAlias; /** * 访问公钥库的密码 */ private String storePass; /** * 证书生成路径 */ private String licensePath; /** * 密钥库存储路径 */ private String publicKeysStorePath; /** * 是否启用license认证 */ private Boolean enableLicense; }5.2 自动配置类通过@Configuration实现自动配置,注入校验器 Bean:@Configuration @AllArgsConstructor @EnableConfigurationProperties(LicenseConfigProperties.class) public class LicenseAutoConfiguration { private final LicenseConfigProperties licenseConfigProperties; // 注入LicenseVerify Bean,启动时执行install方法 @Bean(initMethod = "install") public LicenseVerify licenseVerify() { LicenseVerifyParam param = new LicenseVerifyParam(); param.setSubject(licenseConfigProperties.getSubject()); param.setPublicAlias(licenseConfigProperties.getPublicAlias()); param.setStorePass(licenseConfigProperties.getStorePass()); param.setLicensePath(licenseConfigProperties.getLicensePath()); param.setPublicKeysStorePath(licenseConfigProperties.getPublicKeysStorePath()); return new LicenseVerify(param, licenseConfigProperties.getEnableLicense()); } }5.3 AOP 拦截实现通过自定义注解@RequireLicense和 AOP 拦截,实现接口级别的证书校验:5.3.1 自定义注解/** * 标记需要证书校验的接口方法 */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RequireLicense { boolean value() default true; // 是否启用校验(默认启用) }5.3.2 AOP 拦截逻辑@Slf4j @Aspect @Component public class RequireLicenseAspect { private final LicenseVerify licenseVerify; private final LicenseConfigProperties properties; public RequireLicenseAspect(LicenseVerify licenseVerify, LicenseConfigProperties properties) { this.licenseVerify = licenseVerify; this.properties = properties; } // 拦截所有添加@RequireLicense注解的方法 @Around("@annotation(requireLicense)") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point, RequireLicense requireLicense) throws Throwable { // 注解禁用校验或全局禁用校验,直接执行方法 if (!requireLicense.value() || !properties.getEnableLicense()) { log.info("接口[{}]跳过证书校验", point.getSignature().getName()); return point.proceed(); } // 执行证书校验 boolean verifyResult = licenseVerify.verify(); if (verifyResult) { return point.proceed(); // 校验通过,执行原方法 } else { throw new LicenseInterceptException("接口调用失败:证书未授权或已过期"); } } }5.4 注册自动配置类在src/main/resources/META-INF目录下创建spring.factories文件,指定自动配置类:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ com.jcq.license.autoconfigure.LicenseAutoConfiguration,\ com.jcq.license.verify.aop.RequireLicenseAspect六、Starter 打包配置为确保其他项目引用 Starter 时能正常加载类,需修改pom.xml的构建配置:<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <!-- 跳过Spring Boot默认的可执行JAR打包(避免类路径嵌套在BOOT-INF下) --> <configuration> <skip>true</skip> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>原因:默认情况下,Spring Boot 插件会将类打包到BOOT-INF/classes目录下,导致其他项目引用时无法通过常规类路径加载类。设置skip=true后,会生成标准的 JAR 包,类路径更友好。七、使用示例7.1 引入依赖在目标项目的pom.xml中引入自定义 Starter:<dependency> <groupId>com.jcq</groupId> <artifactId>license-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>7.2 配置参数在application.yml中配置证书相关参数,配置时idea会弹出提示:license: subject: 企业版软件授权证书 public-alias: publiccert store-pass: 123456q license-path: classpath:license.lic # 证书文件存放路径 public-keys-store-path: classpath:publicCerts.store # 公钥库路径 enable-license: true # 启用证书校验7.3 接口使用注解在需要授权的接口方法上添加@RequireLicense注解:@RestController @RequestMapping("/api") public class DemoController { @GetMapping("/sensitive") @RequireLicense // 需要证书校验 public String sensitiveOperation() { return "敏感操作执行成功(已授权)"; } @GetMapping("/public") @RequireLicense(false) // 禁用校验(即使全局启用也会跳过) public String publicOperation() { return "公开操作执行成功(无需授权)"; } }八、总结本文通过自定义 Spring Boot Starter 整合 TrueLicense,实现了一套灵活的证书授权方案,核心优势包括:可插拔性:通过 Starter 封装,引入依赖即可使用,无需重复开发。灵活性:支持全局开关和接口级开关,方便测试环境跳过校验。安全性:基于非对称加密和硬件绑定,防止证书伪造和非法传播。易维护:授权到期后只需替换证书文件,无需修改代码或重启服务。实际项目中可根据需求扩展校验维度(如 CPU 序列号、内存大小等),进一步增强授权的安全性。附录:核心类说明类名作用LicenseCreator证书生成工具类LicenseVerify证书校验核心类(启动校验 + 实时校验)LicenseConfigProperties配置参数映射类LicenseAutoConfigurationStarter 自动配置类RequireLicense接口校验注解RequireLicenseAspectAOP 拦截器(实现接口级校验)完整源码可参考 GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/Jucunqi/license-spring-boot-starter.git(示例地址)。 -
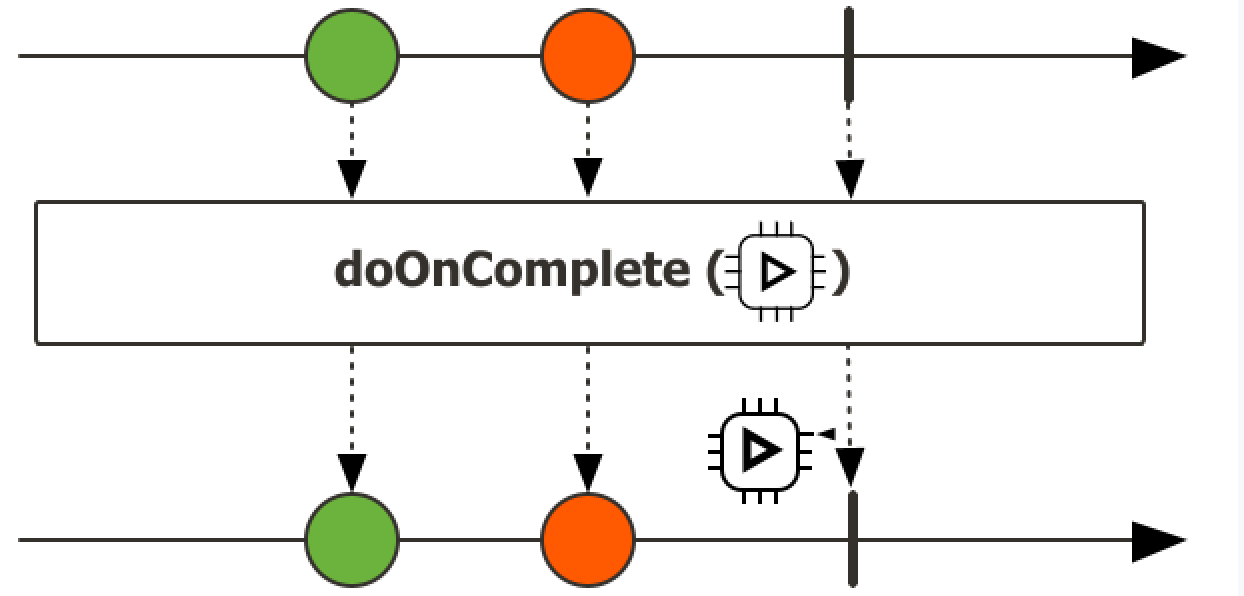
 响应式编程学习笔记 响应式编程1、Reactor核心前置知识1、Lambda2、Function根据出参,入参分类1、有入参,有出参 --> FunctionFunction<String, Integer> function = a -> Integer.parseInt(a);2、有入参,无出参Consumer<String> consumer = a -> System.out.println(a);3、无入参,有出参Supplier<String> supplier = () -> UUID.randomUUID().toString();4、无入参,无出参Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("xixi"); 3、StreamAPI流式操作,三大步骤1、创建流Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();2、中间操作(intermediate operation),可以有多个filter,map,mapToInt,mapToLong,mapToDouble,flatMap,flatMapToInt,flatMapToLong,flatMapToDouble,mapMulti,mapMultiToInt,mapMultiToLong,mapMultiToDouble,peek...3、终止操作(terminal operation),只能有一个forEach,forEachOrdered,toArray,toArray,reduce,collect,toList,min,max,count,anyMatch,findFirst,findAny...流式操作是否并发? // 流的三大部份 // 1.创建流 2.N个中间操作 3.一个终止操作 Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Object> buildStream = Stream.builder().add(1).add(2).add(3).build(); Stream<Object> concatStream = Stream.concat(integerStream, buildStream); Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream(); List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); System.out.println("main线程: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); // 流是不是并发操作? 答:默认单线程,可以通过parallel开启多线程,但是如果开启多线程,则需要自身注意线程安全问题 long count = list.stream() .parallel() // 开启多线程 并发流 .filter(i -> { // resultList.add(i); // 开启多线程,不能这样写,要保证流里面的数据是无状态的,即流里面的数据只在流内部使用 // 可以计算完成以后返回出去,但是不能在内部又引用外部的数据,可能会出现问题 System.out.println("filter线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); return i > 2; }) .count(); System.out.println(resultList);注意: 要保证流里面的数据是无状态的中间操作:filter:过滤,挑出我们要的元素takeWhile示例List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) .filter(a -> a > 2) // 无条件遍历 .toList(); System.out.println(collect); List<Integer> collect1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) .takeWhile(a -> a < 2) // 当条件不满足时,直接返回 .toList(); System.out.println(collect1);map:映射,一对一映射mapToInt,MapToDouble..flatMap: 打散、散列、展开,一对多映射...终止操作:forEach、forEachOrdered、toArray、reduce、collect、toList、min、 max、count、anyMatch、allMatch、noneMatch、findFirst、findAny、iterator4、Reactive Stream目的:通过全异步的方式,加缓冲区构建一个实时的数据流系统。kafka,mq能构建大型的分布式响应系统,缺少本地化分布式响应系统方案jvm推出Reactive Stream,让所有异步线程能够互相监听消息,处理消息,构建实时消息处理流Api Component:1、Publisher:发布者2、Subscriber:订阅者3、Processor:处理器响应式编程总结:1、底层:基于数据缓冲队列+消息驱动模型+异步回调机制2、编码:流式编程+链式调用+生命式API3、效果:优雅全异步+消息实时处理+高吞吐量+占用少量资源与传统写法对比:传统写法痛点:以前要做一个高并发系统:缓存、异步、队列,手动控制整个逻辑现在:全自动控制整个逻辑Reactor1、快速上手介绍Reactor 是一个用于JVM的完全非阻塞的响应式编程框架,具备高效的需求管理(即对 “背压(backpressure)”的控制)能力。它与 Java 8 函数式 API 直接集成,比如 CompletableFuture, Stream, 以及 Duration。它提供了异步序列 API Flux(用于[N]个元素)和 Mono(用于 [0|1]个元素),并完全遵循和实现了“响应式扩展规范”(Reactive Extensions Specification)。Reactor 的 reactor-ipc 组件还支持非阻塞的进程间通信(inter-process communication, IPC)。 Reactor IPC 为 HTTP(包括 Websockets)、TCP 和 UDP 提供了支持背压的网络引擎,从而适合 应用于微服务架构。并且完整支持响应式编解码(reactive encoding and decoding)。依赖<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-bom</artifactId> <version>2023.0.0</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement><dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>2、响应式编程响应式编程是一种关注于数据流(data streams)和变化传递(propagation of change)的异步编程方式。 这意味着它可以用既有的编程语言表达静态(如数组)或动态(如事件源)的数据流。3、核心特性1、Mono和FluxMono: 0|1 数据流Flux: N数据流响应式流:元素(内容) + 信号(完成/异常);2、subscribe()自定义流的信号感知回调.subscribe( System.out::println // 消费方法 , throwable -> System.out.println(throwable.getMessage()) // 感知异常 , () -> System.out.println("complete") // 感知正常结束 ); // 流只有被订阅了才会执行,否则没有任何操作自定义消费者.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<String>() { // 自定义消费者 @Override protected void hookOnSubscribe(Subscription subscription) { System.out.println("被订阅"); requestUnbounded(); } @Override protected void hookOnNext(String value) { System.out.println("下个元素"); } @Override protected void hookOnComplete() { System.out.println("完成信号"); } @Override protected void hookOnError(Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("异常信号"); } @Override protected void hookOnCancel() { System.out.println("结束信号"); } @Override protected void hookFinally(SignalType type) { System.out.println("终止信号"); } });3、流的取消消费者调用 cancle() 取消流的订阅;4、自定义消费者推荐直接编写jdk自带的BaseSubscriber的实现类5、背压(back pressure)和请求重塑(reshape requests)buffer/** * 缓冲区 */ private static void bufferTest() { Flux.range(1, 10).buffer(3).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v的类型:" + v.getClass() + "的值:" + v)); }limitRate/** * 测试limitRate */ private static void limitTest() { Flux.range(1,1000) .log() .limitRate(100) // 一次预取100个元素 75%预取策略,第一次取100个如果75%已经处理,继续请求新的75%数据 .subscribe(System.out::println); }6、以编程方式创建序列-SinkSink.nextSink.complete1、同步环境-generate/** * 通过generate创建序列 */ private static void generateTest() { List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9); Flux.generate(() -> 0, // 初始值 (i, a) -> { a.next(list.get(i)); // 把元素放入通道 if (i == list.size() - 1) { a.complete(); // 完成 } return ++i; // 下次回调的元素 } ) .subscribe(System.out::println); }2、多线程-create/** * 通过create创建序列,create适用与多线程环境,generate适用于单线程环境 */ private static void createTest() { Flux.create(sink -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { sink.next("2"); } }).subscribe(System.out::println); }7、handle自定义流中的处理规则/** * handle自定义处理 */ private static void handleTest() { Flux.range(1, 10) .handle((value,sink) -> { System.out.println("接收到value:" + value); sink.next("haha_" + value); }) .subscribe(); }8、自定义线程调度响应式:响应式编程: 全异步、消息、事件回调默认还是用当前线程,生成整个流、发布流、流操作/** * 自定义线程测试 */ private static void threadTest() { // 响应式编程:全异步,消息,回调机制 Schedulers.boundedElastic(); // 有界的,弹性线程池 Schedulers.single(); // 单线程 Schedulers.immediate(); // 都在同一个当前线程(默认) Scheduler scheduler = Schedulers.newParallel("my-parallel"); Flux<Integer> flux = Flux.range(1, 10) .publishOn(scheduler) .log(); flux.subscribe(); }9、异常处理命令式编程:常见的错误处理方式Catch and return a static default value. 捕获异常返回一个静态默认值try { return doSomethingDangerous(10); } catch (Throwable error) { return "RECOVERED"; }onErrorReturn: 实现上面效果,错误的时候返回一个值●1、吃掉异常,消费者无异常感知●2、返回一个兜底默认值●3、流正常完成;Catch and execute an alternative path with a fallback method.吃掉异常,执行一个兜底方法;try { return doSomethingDangerous(10); } catch (Throwable error) { return doOtherthing(10); }onErrorResume●1、吃掉异常,消费者无异常感知●2、调用一个兜底方法●3、流正常完成Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).onErrorResume(err -> Mono.just("哈哈-777")) .subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));Catch and dynamically compute a fallback value. 捕获并动态计算一个返回值根据错误返回一个新值try { Value v = erroringMethod(); return MyWrapper.fromValue(v); } catch (Throwable error) { return MyWrapper.fromError(error); }.onErrorResume(err -> Flux.error(new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+":炸了")))●1、吃掉异常,消费者有感知●2、调用一个自定义方法●3、流异常完成Catch, wrap to a BusinessException, and re-throw.捕获并包装成一个业务异常,并重新抛出try { return callExternalService(k); } catch (Throwable error) { throw new BusinessException("oops, SLA exceeded", error); }包装重新抛出异常: 推荐用 .onErrorMap●1、吃掉异常,消费者有感知●2、抛新异常●3、流异常完成.onErrorResume(err -> Flux.error(new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+":炸了"))) Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorMap(err-> new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+": 又炸了...")) .subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));Catch, log an error-specific message, and re-throw.捕获异常,记录特殊的错误日志,重新抛出try { return callExternalService(k); } catch (RuntimeException error) { //make a record of the error log("uh oh, falling back, service failed for key " + k); throw error; }Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("err已被记录 = " + err); }).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));●异常被捕获、做自己的事情●不影响异常继续顺着流水线传播●1、不吃掉异常,只在异常发生的时候做一件事,消费者有感知Use the finally block to clean up resources or a Java 7 “try-with-resource” construct. Flux.just(1, 2, 3, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("err已被记录 = " + err); }) .doFinally(signalType -> { System.out.println("流信号:"+signalType); })忽略当前异常,仅通知记录,继续推进Flux.just(1,2,3,0,5) .map(i->10/i) .onErrorContinue((err,val)->{ System.out.println("err = " + err); System.out.println("val = " + val); System.out.println("发现"+val+"有问题了,继续执行其他的,我会记录这个问题"); }) //发生 .subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v), err-> System.out.println("err = " + err));10、常用操作filter、flatMap、concatMap、flatMapMany、transform、defaultIfEmpty、switchIfEmpty、concat、concatWith、merge、mergeWith、mergeSequential、zip、zipWith...2、Spring Webflux0、组件对比API功能Servlet-阻塞式WebWebFlux-响应式Web前端控制器DispatcherServletDispatcherHandler处理器ControllerWebHandler/Controller请求、响应ServletRequest、ServletResponseServerWebExchange:ServerHttpRequest、ServerHttpResponse过滤器Filter(HttpFilter)WebFilter异常处理器HandlerExceptionResolverDispatchExceptionHandlerWeb配置@EnableWebMvc@EnableWebFlux自定义配置WebMvcConfigurerWebFluxConfigurer返回结果任意Mono、Flux、任意发送REST请求RestTemplateWebClientMono: 返回0|1 数据流Flux:返回N数据流1、WebFlux底层基于Netty实现的Web容器与请求/响应处理机制参照:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux.html2、引入<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.1.6</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>Context 响应式上下文数据传递; 由下游传播给上游;以前: 浏览器 --> Controller --> Service --> Dao: 阻塞式编程现在: Dao(数据源查询对象【数据发布者】) --> Service --> Controller --> 浏览器: 响应式大数据流程: 从一个数据源拿到大量数据进行分析计算;ProductVistorDao.loadData() .distinct() .map() .filter() .handle().subscribe();;//加载最新的商品浏览数据3、Reactor Core1、HttpHandler、HttpServer** * 测试webflux * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/1/16 */ public class FluxMainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { HttpHandler handler = (ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) -> { URI uri = request.getURI(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "请求进来: " + uri); //编写请求处理的业务,给浏览器写一个内容 URL + "Hello~!" // response.getHeaders(); //获取响应头 // response.getCookies(); //获取Cookie // response.getStatusCode(); //获取响应状态码; // response.bufferFactory(); //buffer工厂 // response.writeWith() //把xxx写出去 // response.setComplete(); //响应结束 //创建 响应数据的 DataBuffer DataBufferFactory factory = response.bufferFactory(); String result = "Hello world"; //数据Buffer DataBuffer buffer = factory.wrap(result.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 需要一个 DataBuffer 的发布者 return response.writeWith(Flux.just(buffer)); }; //2、启动一个服务器,监听8080端口,接受数据,拿到数据交给 HttpHandler 进行请求处理 ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter adapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(handler); //3、启动Netty服务器 HttpServer.create() .host("localhost") .port(8080) .handle(adapter) //用指定的处理器处理请求 .bindNow(); //现在就绑定 System.out.println("服务器启动完成....监听8080,接受请求"); System.in.read(); System.out.println("服务器停止...."); } }4、DispatcherHandlerSpringMVC: DispatcherServlet;SpringWebFlux: DispatcherHandler1、请求处理流程HandlerMapping:请求映射处理器; 保存每个请求由哪个方法进行处理HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器;反射执行目标方法HandlerResultHandler:处理器结果处理器;SpringMVC: DispatcherServlet 有一个 doDispatch() 方法,来处理所有请求;WebFlux: DispatcherHandler 有一个 handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) 方法,来处理所有请求;public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return createNotFoundError(); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(exchange.getRequest())) { return handlePreFlight(exchange); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) //拿到所有的 handlerMappings .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) //找每一个mapping看谁能处理请求 .next() //直接触发获取元素; 拿到流的第一个元素; 找到第一个能处理这个请求的handlerAdapter .switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError()) //如果没拿到这个元素,则响应404错误; .onErrorResume(ex -> handleDispatchError(exchange, ex)) //异常处理,一旦前面发生异常,调用处理异常 .flatMap(handler -> handleRequestWith(exchange, handler)); //调用方法处理请求,得到响应结果 }1、请求和响应都封装在 ServerWebExchange 对象中,由handle方法进行处理2、如果没有任何的请求映射器; 直接返回一个: 创建一个未找到的错误; 404; 返回Mono.error;终结流3、跨域工具,是否跨域请求,跨域请求检查是否复杂跨域,需要预检请求;4、Flux流式操作,先找到HandlerMapping,再获取handlerAdapter,再用Adapter处理请求,期间的错误由onErrorResume触发回调进行处理;源码中的核心两个:handleRequestWith: 编写了handlerAdapter怎么处理请求handleResult: String、User、ServerSendEvent、Mono、Flux ...concatMap: 先挨个元素变,然后把变的结果按照之前元素的顺序拼接成一个完整流private <R> Mono<R> createNotFoundError() { Exception ex = new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); return Mono.error(ex); } Mono.defer(() -> { Exception ex = new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); return Mono.error(ex); }); //有订阅者,且流被激活后就动态调用这个方法; 延迟加载; 5、注解开发1、目标方法传参https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux/controller/ann-methods/arguments.htmlController method argumentDescriptionServerWebExchange封装了请求和响应对象的对象; 自定义获取数据、自定义响应ServerHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse请求、响应WebSession访问Session对象java.security.Principal org.springframework.http.HttpMethod请求方式java.util.Locale国际化java.util.TimeZone + java.time.ZoneId时区@PathVariable路径变量@MatrixVariable矩阵变量@RequestParam请求参数@RequestHeader请求头;@CookieValue获取Cookie@RequestBody获取请求体,Post、文件上传HttpEntity封装后的请求对象@RequestPart获取文件上传的数据 multipart/form-data.java.util.Map, org.springframework.ui.Model, and org.springframework.ui.ModelMap.Map、Model、ModelMap@ModelAttribute Errors, BindingResult数据校验,封装错误SessionStatus + class-level @SessionAttributes UriComponentsBuilderFor preparing a URL relative to the current request’s host, port, scheme, and context path. See URI Links.@SessionAttribute @RequestAttribute转发请求的请求域数据Any other argument所有对象都能作为参数:1、基本类型 ,等于标注@RequestParam 2、对象类型,等于标注 @ModelAttribute2、返回值写法sse和websocket区别:SSE:单工;请求过去以后,等待服务端源源不断的数据websocket:双工: 连接建立后,可以任何交互;Controller method return valueDescription@ResponseBody把响应数据写出去,如果是对象,可以自动转为jsonHttpEntity, ResponseEntityResponseEntity:支持快捷自定义响应内容HttpHeaders没有响应内容,只有响应头ErrorResponse快速构建错误响应ProblemDetailSpringBoot3;String就是和以前的使用规则一样;forward: 转发到一个地址redirect: 重定向到一个地址配合模板引擎View直接返回视图对象java.util.Map, org.springframework.ui.Model以前一样@ModelAttribute以前一样Rendering新版的页面跳转API; 不能标注 @ResponseBody 注解void仅代表响应完成信号Flux, Observable, or other reactive type使用 text/event-stream 完成SSE效果Other return values未在上述列表的其他返回值,都会当成给页面的数据;6、文件上传https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux/controller/ann-methods/multipart-forms.htmlclass MyForm { private String name; private MultipartFile file; // ... } @Controller public class FileUploadController { @PostMapping("/form") public String handleFormUpload(MyForm form, BindingResult errors) { // ... } }现在@PostMapping("/") public String handle(@RequestPart("meta-data") Part metadata, @RequestPart("file-data") FilePart file) { // ... }7、错误处理 @ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class) public String error(ArithmeticException exception){ System.out.println("发生了数学运算异常"+exception); //返回这些进行错误处理; // ProblemDetail: 建造者:声明式编程、链式调用 // ErrorResponse : return "炸了,哈哈..."; }8、自定义Flux配置 WebFluxConfigurer容器中注入这个类型的组件,重写底层逻辑@Configuration public class MyWebConfiguration { //配置底层 @Bean public WebFluxConfigurer webFluxConfigurer(){ return new WebFluxConfigurer() { @Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) { registry.addMapping("/**") .allowedHeaders("*") .allowedMethods("*") .allowedOrigins("localhost"); } }; } }9、Filter@Component public class MyWebFilter implements WebFilter { @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) { ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse(); System.out.println("请求处理放行到目标方法之前..."); Mono<Void> filter = chain.filter(exchange); //放行 //流一旦经过某个操作就会变成新流 Mono<Void> voidMono = filter.doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("目标方法异常以后..."); }) // 目标方法发生异常后做事 .doFinally(signalType -> { System.out.println("目标方法执行以后..."); });// 目标方法执行之后 //上面执行不花时间。 return voidMono; //看清楚返回的是谁!!! } }3、R2DBC1、手写R2DBC用法:1、导入驱动: 导入连接池(r2dbc-pool)、导入驱动(r2dbc-mysql )2、使用驱动提供的API操作引入依赖<dependency> <groupId>io.asyncer</groupId> <artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId> <version>1.0.5</version> </dependency>手写代码public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建mysql配置 MySqlConnectionConfiguration configuration = MySqlConnectionConfiguration.builder() .host("localhost") .port(3306) .username("root") .password("12345678") .database("test") .build(); // 获取mysql连接工厂 MySqlConnectionFactory factory = MySqlConnectionFactory.from(configuration); Mono.from( factory.create() .flatMapMany(conn -> conn .createStatement("select * from customers where customer_id = ?") .bind(0, 1L) .execute() ).flatMap(result -> result.map(readable -> { return new Customers(((Integer) readable.get("customer_id")), Objects.requireNonNull(readable.get("customer_name")).toString()); })) ).subscribe(System.out::println); System.in.read(); }2、Spring Data R2DBC提升生产力方式的 响应式数据库操作0、整合1、导入依赖 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.asyncer/r2dbc-mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>io.asyncer</groupId> <artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId> <version>1.0.5</version> </dependency> <!-- 响应式 Spring Data R2dbc--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc</artifactId> </dependency>2、编写配置spring: r2dbc: password: 123456 username: root url: r2dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test name: test3、@Autowired private R2dbcEntityTemplate template; /** * 测试template // 适合单表操作,复杂sql不好编写 * @throws IOException io异常 */ @Test public void springDataR2dbcTest() throws IOException { // 1. 构建查询条件 Criteria criteria = Criteria .empty() .and("project_leader") .is("1"); // 构建Query对象 Query query = Query .query(criteria); // 查询数据 template.select(query, com.jcq.r2dbc.eneity.Test.class) .subscribe(test -> System.out.println("test = " + test)); System.out.println(System.in.read()); } @Autowired private DatabaseClient databaseClient; /** * 测试databaseClient // 更底层,适合复杂sql 比如join */ @Test public void databaseClientTest() throws IOException { databaseClient.sql("select * from test where id in (?,?)") .bind(0, 1) .bind(1, 2) .fetch() // 抓取数据 .all() // 抓取所有数据 .map(a -> new com.jcq.r2dbc.eneity.Test(((Integer) a.get("id")),a.get("project_leader").toString())) .subscribe(a -> System.out.println("a = " + a)); System.out.println(System.in.read()); }1、声明式接口:R2dbcRepositoryRepository接口@Repository public interface TAutherRepository extends R2dbcRepository<TAuther,Long> { // 根据命名实现sql Flux<TAuther> findAllByIdAndNameLike(Long id,String name); @Query("select * from t_author") Flux<TAuther> queryList(); } 自定义Converter@ReadingConverter // 读取数据库的时候,吧row转成 TBook public class TBookConverter implements Converter<Row, TBook> { @Override public TBook convert(Row source) { TBook tBook = new TBook(); tBook.setId((Long) source.get("id")); tBook.setTitle((String) source.get("title")); tBook.setAuthorId((Long) source.get("author_id")); Object instance = source.get("publish_time"); System.out.println(instance); ZonedDateTime instance1 = (ZonedDateTime) instance; tBook.setPublishTime(instance1.toInstant()); TAuther tAuther = new TAuther(); tAuther.setName(source.get("name", String.class)); tBook.setTAuther(tAuther); return tBook; } }配置生效@Configuration public class R2DbcConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public R2dbcCustomConversions r2dbcCustomConversions() { return R2dbcCustomConversions.of(MySqlDialect.INSTANCE, new TBookConverter()); } } 3、编程式组件R2dbcEntityTemplateDatabaseClient4、最佳实践最佳实践: 提升生产效率的做法1、Spring Data R2DBC,基础的CRUD用 R2dbcRepository 提供好了2、自定义复杂的SQL(单表): @Query;3、多表查询复杂结果集: DatabaseClient 自定义SQL及结果封装;@Query + 自定义 Converter 实现结果封装经验:1-1:1-N 关联关系的封装都需要自定义结果集的方式Spring Data R2DBC:自定义Converter指定结果封装DatabaseClient:贴近底层的操作进行封装; 见下面代码MyBatis: 自定义 ResultMap 标签去来封装databaseClient.sql("select b.*,t.name as name from t_book b " + "LEFT JOIN t_author t on b.author_id = t.id " + "WHERE b.id = ?") .bind(0, 1L) .fetch() .all() .map(row-> { String id = row.get("id").toString(); String title = row.get("title").toString(); String author_id = row.get("author_id").toString(); String name = row.get("name").toString(); TBook tBook = new TBook(); tBook.setId(Long.parseLong(id)); tBook.setTitle(title); TAuthor tAuthor = new TAuthor(); tAuthor.setName(name); tAuthor.setId(Long.parseLong(author_id)); tBook.setAuthor(tAuthor); return tBook; }) .subscribe(tBook -> System.out.println("tBook = " + tBook));
响应式编程学习笔记 响应式编程1、Reactor核心前置知识1、Lambda2、Function根据出参,入参分类1、有入参,有出参 --> FunctionFunction<String, Integer> function = a -> Integer.parseInt(a);2、有入参,无出参Consumer<String> consumer = a -> System.out.println(a);3、无入参,有出参Supplier<String> supplier = () -> UUID.randomUUID().toString();4、无入参,无出参Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("xixi"); 3、StreamAPI流式操作,三大步骤1、创建流Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();2、中间操作(intermediate operation),可以有多个filter,map,mapToInt,mapToLong,mapToDouble,flatMap,flatMapToInt,flatMapToLong,flatMapToDouble,mapMulti,mapMultiToInt,mapMultiToLong,mapMultiToDouble,peek...3、终止操作(terminal operation),只能有一个forEach,forEachOrdered,toArray,toArray,reduce,collect,toList,min,max,count,anyMatch,findFirst,findAny...流式操作是否并发? // 流的三大部份 // 1.创建流 2.N个中间操作 3.一个终止操作 Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Object> buildStream = Stream.builder().add(1).add(2).add(3).build(); Stream<Object> concatStream = Stream.concat(integerStream, buildStream); Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream(); List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); System.out.println("main线程: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); // 流是不是并发操作? 答:默认单线程,可以通过parallel开启多线程,但是如果开启多线程,则需要自身注意线程安全问题 long count = list.stream() .parallel() // 开启多线程 并发流 .filter(i -> { // resultList.add(i); // 开启多线程,不能这样写,要保证流里面的数据是无状态的,即流里面的数据只在流内部使用 // 可以计算完成以后返回出去,但是不能在内部又引用外部的数据,可能会出现问题 System.out.println("filter线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); return i > 2; }) .count(); System.out.println(resultList);注意: 要保证流里面的数据是无状态的中间操作:filter:过滤,挑出我们要的元素takeWhile示例List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) .filter(a -> a > 2) // 无条件遍历 .toList(); System.out.println(collect); List<Integer> collect1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) .takeWhile(a -> a < 2) // 当条件不满足时,直接返回 .toList(); System.out.println(collect1);map:映射,一对一映射mapToInt,MapToDouble..flatMap: 打散、散列、展开,一对多映射...终止操作:forEach、forEachOrdered、toArray、reduce、collect、toList、min、 max、count、anyMatch、allMatch、noneMatch、findFirst、findAny、iterator4、Reactive Stream目的:通过全异步的方式,加缓冲区构建一个实时的数据流系统。kafka,mq能构建大型的分布式响应系统,缺少本地化分布式响应系统方案jvm推出Reactive Stream,让所有异步线程能够互相监听消息,处理消息,构建实时消息处理流Api Component:1、Publisher:发布者2、Subscriber:订阅者3、Processor:处理器响应式编程总结:1、底层:基于数据缓冲队列+消息驱动模型+异步回调机制2、编码:流式编程+链式调用+生命式API3、效果:优雅全异步+消息实时处理+高吞吐量+占用少量资源与传统写法对比:传统写法痛点:以前要做一个高并发系统:缓存、异步、队列,手动控制整个逻辑现在:全自动控制整个逻辑Reactor1、快速上手介绍Reactor 是一个用于JVM的完全非阻塞的响应式编程框架,具备高效的需求管理(即对 “背压(backpressure)”的控制)能力。它与 Java 8 函数式 API 直接集成,比如 CompletableFuture, Stream, 以及 Duration。它提供了异步序列 API Flux(用于[N]个元素)和 Mono(用于 [0|1]个元素),并完全遵循和实现了“响应式扩展规范”(Reactive Extensions Specification)。Reactor 的 reactor-ipc 组件还支持非阻塞的进程间通信(inter-process communication, IPC)。 Reactor IPC 为 HTTP(包括 Websockets)、TCP 和 UDP 提供了支持背压的网络引擎,从而适合 应用于微服务架构。并且完整支持响应式编解码(reactive encoding and decoding)。依赖<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-bom</artifactId> <version>2023.0.0</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement><dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>2、响应式编程响应式编程是一种关注于数据流(data streams)和变化传递(propagation of change)的异步编程方式。 这意味着它可以用既有的编程语言表达静态(如数组)或动态(如事件源)的数据流。3、核心特性1、Mono和FluxMono: 0|1 数据流Flux: N数据流响应式流:元素(内容) + 信号(完成/异常);2、subscribe()自定义流的信号感知回调.subscribe( System.out::println // 消费方法 , throwable -> System.out.println(throwable.getMessage()) // 感知异常 , () -> System.out.println("complete") // 感知正常结束 ); // 流只有被订阅了才会执行,否则没有任何操作自定义消费者.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<String>() { // 自定义消费者 @Override protected void hookOnSubscribe(Subscription subscription) { System.out.println("被订阅"); requestUnbounded(); } @Override protected void hookOnNext(String value) { System.out.println("下个元素"); } @Override protected void hookOnComplete() { System.out.println("完成信号"); } @Override protected void hookOnError(Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("异常信号"); } @Override protected void hookOnCancel() { System.out.println("结束信号"); } @Override protected void hookFinally(SignalType type) { System.out.println("终止信号"); } });3、流的取消消费者调用 cancle() 取消流的订阅;4、自定义消费者推荐直接编写jdk自带的BaseSubscriber的实现类5、背压(back pressure)和请求重塑(reshape requests)buffer/** * 缓冲区 */ private static void bufferTest() { Flux.range(1, 10).buffer(3).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v的类型:" + v.getClass() + "的值:" + v)); }limitRate/** * 测试limitRate */ private static void limitTest() { Flux.range(1,1000) .log() .limitRate(100) // 一次预取100个元素 75%预取策略,第一次取100个如果75%已经处理,继续请求新的75%数据 .subscribe(System.out::println); }6、以编程方式创建序列-SinkSink.nextSink.complete1、同步环境-generate/** * 通过generate创建序列 */ private static void generateTest() { List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9); Flux.generate(() -> 0, // 初始值 (i, a) -> { a.next(list.get(i)); // 把元素放入通道 if (i == list.size() - 1) { a.complete(); // 完成 } return ++i; // 下次回调的元素 } ) .subscribe(System.out::println); }2、多线程-create/** * 通过create创建序列,create适用与多线程环境,generate适用于单线程环境 */ private static void createTest() { Flux.create(sink -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { sink.next("2"); } }).subscribe(System.out::println); }7、handle自定义流中的处理规则/** * handle自定义处理 */ private static void handleTest() { Flux.range(1, 10) .handle((value,sink) -> { System.out.println("接收到value:" + value); sink.next("haha_" + value); }) .subscribe(); }8、自定义线程调度响应式:响应式编程: 全异步、消息、事件回调默认还是用当前线程,生成整个流、发布流、流操作/** * 自定义线程测试 */ private static void threadTest() { // 响应式编程:全异步,消息,回调机制 Schedulers.boundedElastic(); // 有界的,弹性线程池 Schedulers.single(); // 单线程 Schedulers.immediate(); // 都在同一个当前线程(默认) Scheduler scheduler = Schedulers.newParallel("my-parallel"); Flux<Integer> flux = Flux.range(1, 10) .publishOn(scheduler) .log(); flux.subscribe(); }9、异常处理命令式编程:常见的错误处理方式Catch and return a static default value. 捕获异常返回一个静态默认值try { return doSomethingDangerous(10); } catch (Throwable error) { return "RECOVERED"; }onErrorReturn: 实现上面效果,错误的时候返回一个值●1、吃掉异常,消费者无异常感知●2、返回一个兜底默认值●3、流正常完成;Catch and execute an alternative path with a fallback method.吃掉异常,执行一个兜底方法;try { return doSomethingDangerous(10); } catch (Throwable error) { return doOtherthing(10); }onErrorResume●1、吃掉异常,消费者无异常感知●2、调用一个兜底方法●3、流正常完成Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).onErrorResume(err -> Mono.just("哈哈-777")) .subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));Catch and dynamically compute a fallback value. 捕获并动态计算一个返回值根据错误返回一个新值try { Value v = erroringMethod(); return MyWrapper.fromValue(v); } catch (Throwable error) { return MyWrapper.fromError(error); }.onErrorResume(err -> Flux.error(new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+":炸了")))●1、吃掉异常,消费者有感知●2、调用一个自定义方法●3、流异常完成Catch, wrap to a BusinessException, and re-throw.捕获并包装成一个业务异常,并重新抛出try { return callExternalService(k); } catch (Throwable error) { throw new BusinessException("oops, SLA exceeded", error); }包装重新抛出异常: 推荐用 .onErrorMap●1、吃掉异常,消费者有感知●2、抛新异常●3、流异常完成.onErrorResume(err -> Flux.error(new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+":炸了"))) Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorMap(err-> new BusinessException(err.getMessage()+": 又炸了...")) .subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));Catch, log an error-specific message, and re-throw.捕获异常,记录特殊的错误日志,重新抛出try { return callExternalService(k); } catch (RuntimeException error) { //make a record of the error log("uh oh, falling back, service failed for key " + k); throw error; }Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("err已被记录 = " + err); }).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v), err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), () -> System.out.println("流结束"));●异常被捕获、做自己的事情●不影响异常继续顺着流水线传播●1、不吃掉异常,只在异常发生的时候做一件事,消费者有感知Use the finally block to clean up resources or a Java 7 “try-with-resource” construct. Flux.just(1, 2, 3, 4) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("err已被记录 = " + err); }) .doFinally(signalType -> { System.out.println("流信号:"+signalType); })忽略当前异常,仅通知记录,继续推进Flux.just(1,2,3,0,5) .map(i->10/i) .onErrorContinue((err,val)->{ System.out.println("err = " + err); System.out.println("val = " + val); System.out.println("发现"+val+"有问题了,继续执行其他的,我会记录这个问题"); }) //发生 .subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v), err-> System.out.println("err = " + err));10、常用操作filter、flatMap、concatMap、flatMapMany、transform、defaultIfEmpty、switchIfEmpty、concat、concatWith、merge、mergeWith、mergeSequential、zip、zipWith...2、Spring Webflux0、组件对比API功能Servlet-阻塞式WebWebFlux-响应式Web前端控制器DispatcherServletDispatcherHandler处理器ControllerWebHandler/Controller请求、响应ServletRequest、ServletResponseServerWebExchange:ServerHttpRequest、ServerHttpResponse过滤器Filter(HttpFilter)WebFilter异常处理器HandlerExceptionResolverDispatchExceptionHandlerWeb配置@EnableWebMvc@EnableWebFlux自定义配置WebMvcConfigurerWebFluxConfigurer返回结果任意Mono、Flux、任意发送REST请求RestTemplateWebClientMono: 返回0|1 数据流Flux:返回N数据流1、WebFlux底层基于Netty实现的Web容器与请求/响应处理机制参照:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux.html2、引入<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.1.6</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>Context 响应式上下文数据传递; 由下游传播给上游;以前: 浏览器 --> Controller --> Service --> Dao: 阻塞式编程现在: Dao(数据源查询对象【数据发布者】) --> Service --> Controller --> 浏览器: 响应式大数据流程: 从一个数据源拿到大量数据进行分析计算;ProductVistorDao.loadData() .distinct() .map() .filter() .handle().subscribe();;//加载最新的商品浏览数据3、Reactor Core1、HttpHandler、HttpServer** * 测试webflux * @author : jucunqi * @since : 2025/1/16 */ public class FluxMainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { HttpHandler handler = (ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) -> { URI uri = request.getURI(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "请求进来: " + uri); //编写请求处理的业务,给浏览器写一个内容 URL + "Hello~!" // response.getHeaders(); //获取响应头 // response.getCookies(); //获取Cookie // response.getStatusCode(); //获取响应状态码; // response.bufferFactory(); //buffer工厂 // response.writeWith() //把xxx写出去 // response.setComplete(); //响应结束 //创建 响应数据的 DataBuffer DataBufferFactory factory = response.bufferFactory(); String result = "Hello world"; //数据Buffer DataBuffer buffer = factory.wrap(result.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 需要一个 DataBuffer 的发布者 return response.writeWith(Flux.just(buffer)); }; //2、启动一个服务器,监听8080端口,接受数据,拿到数据交给 HttpHandler 进行请求处理 ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter adapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(handler); //3、启动Netty服务器 HttpServer.create() .host("localhost") .port(8080) .handle(adapter) //用指定的处理器处理请求 .bindNow(); //现在就绑定 System.out.println("服务器启动完成....监听8080,接受请求"); System.in.read(); System.out.println("服务器停止...."); } }4、DispatcherHandlerSpringMVC: DispatcherServlet;SpringWebFlux: DispatcherHandler1、请求处理流程HandlerMapping:请求映射处理器; 保存每个请求由哪个方法进行处理HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器;反射执行目标方法HandlerResultHandler:处理器结果处理器;SpringMVC: DispatcherServlet 有一个 doDispatch() 方法,来处理所有请求;WebFlux: DispatcherHandler 有一个 handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) 方法,来处理所有请求;public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return createNotFoundError(); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(exchange.getRequest())) { return handlePreFlight(exchange); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) //拿到所有的 handlerMappings .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) //找每一个mapping看谁能处理请求 .next() //直接触发获取元素; 拿到流的第一个元素; 找到第一个能处理这个请求的handlerAdapter .switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError()) //如果没拿到这个元素,则响应404错误; .onErrorResume(ex -> handleDispatchError(exchange, ex)) //异常处理,一旦前面发生异常,调用处理异常 .flatMap(handler -> handleRequestWith(exchange, handler)); //调用方法处理请求,得到响应结果 }1、请求和响应都封装在 ServerWebExchange 对象中,由handle方法进行处理2、如果没有任何的请求映射器; 直接返回一个: 创建一个未找到的错误; 404; 返回Mono.error;终结流3、跨域工具,是否跨域请求,跨域请求检查是否复杂跨域,需要预检请求;4、Flux流式操作,先找到HandlerMapping,再获取handlerAdapter,再用Adapter处理请求,期间的错误由onErrorResume触发回调进行处理;源码中的核心两个:handleRequestWith: 编写了handlerAdapter怎么处理请求handleResult: String、User、ServerSendEvent、Mono、Flux ...concatMap: 先挨个元素变,然后把变的结果按照之前元素的顺序拼接成一个完整流private <R> Mono<R> createNotFoundError() { Exception ex = new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); return Mono.error(ex); } Mono.defer(() -> { Exception ex = new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); return Mono.error(ex); }); //有订阅者,且流被激活后就动态调用这个方法; 延迟加载; 5、注解开发1、目标方法传参https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux/controller/ann-methods/arguments.htmlController method argumentDescriptionServerWebExchange封装了请求和响应对象的对象; 自定义获取数据、自定义响应ServerHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse请求、响应WebSession访问Session对象java.security.Principal org.springframework.http.HttpMethod请求方式java.util.Locale国际化java.util.TimeZone + java.time.ZoneId时区@PathVariable路径变量@MatrixVariable矩阵变量@RequestParam请求参数@RequestHeader请求头;@CookieValue获取Cookie@RequestBody获取请求体,Post、文件上传HttpEntity封装后的请求对象@RequestPart获取文件上传的数据 multipart/form-data.java.util.Map, org.springframework.ui.Model, and org.springframework.ui.ModelMap.Map、Model、ModelMap@ModelAttribute Errors, BindingResult数据校验,封装错误SessionStatus + class-level @SessionAttributes UriComponentsBuilderFor preparing a URL relative to the current request’s host, port, scheme, and context path. See URI Links.@SessionAttribute @RequestAttribute转发请求的请求域数据Any other argument所有对象都能作为参数:1、基本类型 ,等于标注@RequestParam 2、对象类型,等于标注 @ModelAttribute2、返回值写法sse和websocket区别:SSE:单工;请求过去以后,等待服务端源源不断的数据websocket:双工: 连接建立后,可以任何交互;Controller method return valueDescription@ResponseBody把响应数据写出去,如果是对象,可以自动转为jsonHttpEntity, ResponseEntityResponseEntity:支持快捷自定义响应内容HttpHeaders没有响应内容,只有响应头ErrorResponse快速构建错误响应ProblemDetailSpringBoot3;String就是和以前的使用规则一样;forward: 转发到一个地址redirect: 重定向到一个地址配合模板引擎View直接返回视图对象java.util.Map, org.springframework.ui.Model以前一样@ModelAttribute以前一样Rendering新版的页面跳转API; 不能标注 @ResponseBody 注解void仅代表响应完成信号Flux, Observable, or other reactive type使用 text/event-stream 完成SSE效果Other return values未在上述列表的其他返回值,都会当成给页面的数据;6、文件上传https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/6.0/web/webflux/controller/ann-methods/multipart-forms.htmlclass MyForm { private String name; private MultipartFile file; // ... } @Controller public class FileUploadController { @PostMapping("/form") public String handleFormUpload(MyForm form, BindingResult errors) { // ... } }现在@PostMapping("/") public String handle(@RequestPart("meta-data") Part metadata, @RequestPart("file-data") FilePart file) { // ... }7、错误处理 @ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class) public String error(ArithmeticException exception){ System.out.println("发生了数学运算异常"+exception); //返回这些进行错误处理; // ProblemDetail: 建造者:声明式编程、链式调用 // ErrorResponse : return "炸了,哈哈..."; }8、自定义Flux配置 WebFluxConfigurer容器中注入这个类型的组件,重写底层逻辑@Configuration public class MyWebConfiguration { //配置底层 @Bean public WebFluxConfigurer webFluxConfigurer(){ return new WebFluxConfigurer() { @Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) { registry.addMapping("/**") .allowedHeaders("*") .allowedMethods("*") .allowedOrigins("localhost"); } }; } }9、Filter@Component public class MyWebFilter implements WebFilter { @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) { ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse(); System.out.println("请求处理放行到目标方法之前..."); Mono<Void> filter = chain.filter(exchange); //放行 //流一旦经过某个操作就会变成新流 Mono<Void> voidMono = filter.doOnError(err -> { System.out.println("目标方法异常以后..."); }) // 目标方法发生异常后做事 .doFinally(signalType -> { System.out.println("目标方法执行以后..."); });// 目标方法执行之后 //上面执行不花时间。 return voidMono; //看清楚返回的是谁!!! } }3、R2DBC1、手写R2DBC用法:1、导入驱动: 导入连接池(r2dbc-pool)、导入驱动(r2dbc-mysql )2、使用驱动提供的API操作引入依赖<dependency> <groupId>io.asyncer</groupId> <artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId> <version>1.0.5</version> </dependency>手写代码public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建mysql配置 MySqlConnectionConfiguration configuration = MySqlConnectionConfiguration.builder() .host("localhost") .port(3306) .username("root") .password("12345678") .database("test") .build(); // 获取mysql连接工厂 MySqlConnectionFactory factory = MySqlConnectionFactory.from(configuration); Mono.from( factory.create() .flatMapMany(conn -> conn .createStatement("select * from customers where customer_id = ?") .bind(0, 1L) .execute() ).flatMap(result -> result.map(readable -> { return new Customers(((Integer) readable.get("customer_id")), Objects.requireNonNull(readable.get("customer_name")).toString()); })) ).subscribe(System.out::println); System.in.read(); }2、Spring Data R2DBC提升生产力方式的 响应式数据库操作0、整合1、导入依赖 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.asyncer/r2dbc-mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>io.asyncer</groupId> <artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId> <version>1.0.5</version> </dependency> <!-- 响应式 Spring Data R2dbc--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc</artifactId> </dependency>2、编写配置spring: r2dbc: password: 123456 username: root url: r2dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test name: test3、@Autowired private R2dbcEntityTemplate template; /** * 测试template // 适合单表操作,复杂sql不好编写 * @throws IOException io异常 */ @Test public void springDataR2dbcTest() throws IOException { // 1. 构建查询条件 Criteria criteria = Criteria .empty() .and("project_leader") .is("1"); // 构建Query对象 Query query = Query .query(criteria); // 查询数据 template.select(query, com.jcq.r2dbc.eneity.Test.class) .subscribe(test -> System.out.println("test = " + test)); System.out.println(System.in.read()); } @Autowired private DatabaseClient databaseClient; /** * 测试databaseClient // 更底层,适合复杂sql 比如join */ @Test public void databaseClientTest() throws IOException { databaseClient.sql("select * from test where id in (?,?)") .bind(0, 1) .bind(1, 2) .fetch() // 抓取数据 .all() // 抓取所有数据 .map(a -> new com.jcq.r2dbc.eneity.Test(((Integer) a.get("id")),a.get("project_leader").toString())) .subscribe(a -> System.out.println("a = " + a)); System.out.println(System.in.read()); }1、声明式接口:R2dbcRepositoryRepository接口@Repository public interface TAutherRepository extends R2dbcRepository<TAuther,Long> { // 根据命名实现sql Flux<TAuther> findAllByIdAndNameLike(Long id,String name); @Query("select * from t_author") Flux<TAuther> queryList(); } 自定义Converter@ReadingConverter // 读取数据库的时候,吧row转成 TBook public class TBookConverter implements Converter<Row, TBook> { @Override public TBook convert(Row source) { TBook tBook = new TBook(); tBook.setId((Long) source.get("id")); tBook.setTitle((String) source.get("title")); tBook.setAuthorId((Long) source.get("author_id")); Object instance = source.get("publish_time"); System.out.println(instance); ZonedDateTime instance1 = (ZonedDateTime) instance; tBook.setPublishTime(instance1.toInstant()); TAuther tAuther = new TAuther(); tAuther.setName(source.get("name", String.class)); tBook.setTAuther(tAuther); return tBook; } }配置生效@Configuration public class R2DbcConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public R2dbcCustomConversions r2dbcCustomConversions() { return R2dbcCustomConversions.of(MySqlDialect.INSTANCE, new TBookConverter()); } } 3、编程式组件R2dbcEntityTemplateDatabaseClient4、最佳实践最佳实践: 提升生产效率的做法1、Spring Data R2DBC,基础的CRUD用 R2dbcRepository 提供好了2、自定义复杂的SQL(单表): @Query;3、多表查询复杂结果集: DatabaseClient 自定义SQL及结果封装;@Query + 自定义 Converter 实现结果封装经验:1-1:1-N 关联关系的封装都需要自定义结果集的方式Spring Data R2DBC:自定义Converter指定结果封装DatabaseClient:贴近底层的操作进行封装; 见下面代码MyBatis: 自定义 ResultMap 标签去来封装databaseClient.sql("select b.*,t.name as name from t_book b " + "LEFT JOIN t_author t on b.author_id = t.id " + "WHERE b.id = ?") .bind(0, 1L) .fetch() .all() .map(row-> { String id = row.get("id").toString(); String title = row.get("title").toString(); String author_id = row.get("author_id").toString(); String name = row.get("name").toString(); TBook tBook = new TBook(); tBook.setId(Long.parseLong(id)); tBook.setTitle(title); TAuthor tAuthor = new TAuthor(); tAuthor.setName(name); tAuthor.setId(Long.parseLong(author_id)); tBook.setAuthor(tAuthor); return tBook; }) .subscribe(tBook -> System.out.println("tBook = " + tBook));